Corporate Income Tax (CIT) Incentives
CIT incentives support and encourage the development of businesses of certain types, in certain area, and engaging in certain sectors. In the table below, we’ve provided the CIT rates for different types of enterprises, sectors, and regions.
|
Type |
CIT Rate |
Effective period |
|
Small and low-profit. enterprises (SLPEs)
|
20%
|
2021.1.1- 2022.12.31
2022.1.1 – 2024.12.31 |
|
High and new technology enterprise (HNTEs) & Advanced technology service enterprise (ATSEs) |
15% |
2019.1.1 to 2023.12.31 |
|
Key software enterprises & key integrated circuit enterprises |
10% |
Effective from 2020.1.1 |
|
Western regions of China* |
15% |
Until 2030.12.31 |
| *Main business should be in encouraged industries of the specific region. | ||
Individual Income Tax (IIT) incentives
China offers incentives in certain regions where the effective IIT rate for qualified talents is 15%, though the eligibility and application method vary from each other. Find more information on region-based incentives here.
IIT subsidies for developing talent in certain regions
|
IIT Subsidies for Developing Talent |
||||
|
Type |
Region |
Policy |
Eligibility |
IIT rate |
|
Overseas high-end talents and urgently needed talents*** |
9 cities of Guangdong province – Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Huizhou, Zhaoqing, Jiangmen, Dongguan, and Foshan |
|
Comprehensive income, business income, and subsidy income from selected talent programs and talent projects.
15% (2019.1.1-2023.12.31) |
|
|
High-end and urgently needed talents |
Hainan FTP
|
Cai Shui [2020] No.32 |
Talents may consult with the local authorities or professionals to ensure whether they can be eligible to enjoy these preferential policies.
|
Comprehensive income, business income, and talent subsidy income recognized by the Hainan government.
The portion of their actual IIT burden exceeding 15% will be exempted.*
15% (2020.1.1-2024.12.31)
3%, 10%, 15% (2025-2035)
|
|
Overseas and domestic high-end talents and shortly needed talents |
Zhuhai Hengqin (Guangdong-Macao ICZ)
|
Yue Caishui [2022] No. 19 |
|
Exempt from paying the portion of income tax that exceeds 15 % of their taxable income.**
2021.1.1 - 2025.12.31 |
|
Eligible overseas high-end talents |
Certain areas in Beijing |
State Council |
The detailed implementation measures are yet to be announced.
|
|
|
Foreign high-end and shortly needed talents |
Shanghai Lingang New Area |
|
|
15% |
|
Hong Kong and Macao residents working in Nansha |
Nansha, southernmost district of Guangzhou |
Cai Shui [2022] No. 29 |
|
The portion of IIT which exceeds the tax burden in Hong Kong or Macao shall be exempted.
2022.1.1-2026.12.31 |
|
* Eligible Hainan talents still need to pay IIT according to China’s general IIT rate in the current year first. When the final settlement is made during March 1 to May 31 of the next year, the Hainan tax bureau will refund the portion of the IIT that exceeds 15% of the actual taxable income. **Macao residents working in the ICZ may apply Macao’s IIT rates. *** Applicants should fit the definition of “high-end” and “urgently needed” talents and meet the income condition and contract condition, set out by the municipal governments. |
||||
Value Added Tax (VAT) incentives
VAT incentives for small scale businesses
From January 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023, small-scale taxpayers with monthly sales of under RMB 100,000 (approx. US$14,740) shall be exempted from VAT. Read more details on incentives based on type of businesses.
VAT incentives in specific regions
VAT exemption policy in GBA
From October 1, 2020 to December 31, 2023, income of insurance premium for international shipping derived by insurance enterprises registered in Guangzhou from enterprises registered in Nansha Area of Guangdong FTZ will be exempt from VAT.
Export tax rebates
Containerized cargos to be shipped abroad from the designated 37 ports of shipment and passing through Nansha Bonded Port of Guangzhou and Qianhai Bonded Port of Shenzhen (the place of departure) by qualified export enterprises with qualified transportation enterprises as the carriers, will be eligible for the export tax rebate policy at the port of the shipment.
Incentives in Shanghai Lingang New Area
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2024, enterprises registered in Yangshan Special Comprehensive Bonded Zone (CBZ) of Lingang New Area are exempt from VAT on income derived from providing transportation services, handling services, and warehouse services within the zone.
Tax incentives offered in specific sectors
CIT incentives in specific sectors
| CIT incentives in specific sectors | ||
|
Projects |
Operational period |
CIT exemption |
|
Integrated circuit production enterprise or projects with line width <28 nm |
> 15 years |
Exemption from CIT for 10 years* |
|
Integrated circuit production enterprise or projects with line width <65 nm |
> 15 years |
Exemption for the first 5 years, and a half-rate tax deduction of the 25 % CIT deduction (that is, 12.5 %) in the subsequent 5 years.*
|
|
Integrated circuit production enterprise or projects with line width <130 nm** |
>10 years |
Exemption for the first two years and a half-rate tax reduction (that is, 12.5 %) in the following three years.* |
|
Encouraged enterprises engaging in IC design, equipment, materials, packaging, and testing and software |
|
Exemption for the first 2 years and a half-rate tax reduction (12.5 %) in the following 3 years, starting from the first profit making year of the enterprise.*
|
|
Key IC enterprises and software enterprises |
|
Exemption for the first 5 years and a reduced 10% CIT rate in the following years, starting from the first profit making year of the enterprise. |
|
Eligible environmental protection, energy saving, or water conservation projects. |
|
Exemption for the first 3 years as of the taxable year when the revenue arising from production or operation is first obtained, and taxed at a half rate from the fourth to the sixth year.
|
|
Planting of vegetables, corn, potatoes, oil plants, beans, cotton, hemp, sugar plants, fruit, and nuts;
Breeding of new varieties of crops;
Planting of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs; Cultivation and planting of woods;
Raising of livestock and poultry;
Gathering of forest products;
Agricultural, forestry, husbandry, and fishery service projects such as irrigation, primary processing of agricultural products, veterinarian, promotion of agricultural technology, operations, repair and maintenance of agricultural machinery etc.;
Ocean fishing.
|
|
Could be exempt from CIT |
|
Enterprises engaging in pollution control |
|
15% (January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2023) |
|
Income derived from planting of flowers, tea, and other beverage plants and spiceberries, and income derived from mariculture and inland aquaculture |
|
50% reduction on income tax |
|
**When an encouraged IC manufacturing enterprise that employs integrated circuit line width that is no more than 130 nanometers incurs a loss in a tax year, the enterprise is allowed to carry the loss forward to subsequent years, provided the loss carried forward does not exceed 10 years. (Note: for normal enterprises, the loss carried forward generally cannot exceed five years). *The abovementioned tax incentives count starting from the first profit making year for the IC enterprise, or the first business revenue collection year for the IC project. |
||
Tax incentives to encourage technology innovation
As China endeavors to shift from being a low-end mass manufacturer to a high-end producer, the government has doubled down on encouraging targeted investments in research and development (R&D) and technological innovation.
High and new technology enterprises (HNTEs)
HNTE is one of China’s core tax incentives that encourage innovation. The reduced CIT rate for qualified taxpayer is 15%.
Further, losses of qualified HNTE that occur five years prior to the year in which they become qualified and have not been made up – shall be allowed to be carried forward to subsequent years to be made up, and the maximum carry-forward period is up to 10 years. For normal enterprises, the maximum carry-forward period for losses is only five years.
Meanwhile, HNTEs can enjoy a one-off pre-tax deduction for equipment and instruments (fixed assets other than houses and buildings) newly purchased during the period from October 1, 2022 to December 31, 2022, and such deduction is allowed to be 100 percent weighted.
Qualification and criteria
- Be registered in China (not including Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan) for at least one year;
- Owns the intellectual property (IP) right for the core technology of its key products or services (services) through independent R&D, transfer, donation, merger and acquisition, etc.;
- The core technology of the enterprise’s key products (services) falls within the scope of the areas outlined in the Regions of Advanced Technologies Strongly Supported by the State, which covers more than 200 categories of technologies, products, and services in eight large technological areas;
- The enterprise’s technical personnel engaging in R&D and relevant technological innovation activities constitute more than 10 percent of the total number of employees in the current year; and
- In the last three financial years (the actual operational period for newly established ones), R&D expenditure should account for a certain percentage of the enterprise’s total sales revenue in the same period:
- No less than five percent if the latest annual sales revenue is below RMB 50 million (inclusive, approx. US$7.7 million);
- No less than four percent if the latest annual sales revenue is below between RMB 50 million (approx. US$7.7 million) and RMB 200 million (inclusive, approx. US$30.8 million); and
- No less than three percent if the latest annual sales income is upwards of RMB 200 million (approx. US$30.8 million).
R&D expenditure within China is not less than 60% of the total R&D;
- The ratio of income from high-tech related operations against total income is not lower than 60 percent in the current period;
- The enterprise’s innovation capacity evaluation satisfies the corresponding requirements; and
- The enterprise has no record of major safety or quality incidents or serious environmental violations during the year preceding the application.
Upon obtaining the qualification as an HNTE, the enterprise shall enjoy the HNTE treatment starting from the year when the HNTE certificate is issued.
Technology-based small- and medium-sized enterprises (TSMEs)
A TSME is a sub category of SMEs that conduct technology-based activities, which includes scientific and technological personnel who are involved in R&D activities and obtain IP for creating high-tech products or services.
The losses of the enterprise that occurred five years before the year in which they qualified as a TSME and have not been made up shall be allowed to be carried forward to subsequent years to be made up. The maximum carry-forward period is up to 10 years. Local governments may treat TSMEs as HNTE candidates and provide other incentives to support their growth e.g., the maximum carry-forward period is 13 years for qualified enterprises in Nansha.
Moreover, TSMEs can enjoy super deduction on their R&D expenses. Starting from January 1, 2022, if the R&D expenses of TSMEs do not form intangible assets and are included in the current profits and losses, on the basis of actual deduction, an additional 100 percent of such R&D expenses could be deducted from the taxable income amount; if the R&D expenses have formed intangible assets, they can be amortized before CIT at 200 percent of the actual cost of intangible assets.
It is easier to apply for the TSME status for smaller businesses.
Qualification and criteria
A TSME shall meet all the following requirements:
- Be registered in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan);
- The total number of its employees shall be no more than 500, and either its annual sales income or its total asset amount shall be no more than RMB 200 million (approx. US$30.8 million);
- The products and services provided by it are not included in the prohibited, restricted, or eliminated categories prescribed by the State; and
- There is no occurrence of major safety or major quality accidents and serious violation of environmental law or serious dishonesty in scientific research in the previous year of filling and the present year, and it is not included in the list of enterprises with abnormal operations or the list of enterprises with serious dishonest behaviors in violations of the law.
Scoring requirements for TSME’s
Its comprehensive evaluation score is not less than 60 points in terms of the evaluation indicators for TSMEs, with the score on scientific and technical staff indicator more than 0 point. The evaluation indicators for TSMEs include categories such as, scientific and technical staff, R&D investment, as well as scientific and technological achievement, with a total score of 100.
Exemptions:
- Enterprise that holds an HNTE certificate that has not expired yet;
- Enterprise that has won a state-level science and technology award within the past five years and ranked in the top three;
- Enterprise that has a recognized R&D body at provincial or ministerial level or above; and
- Enterprise has taken the lead in the development of international standards, national standards, or industry standards within the past five years.
HNTE vs TSME
In comparison to HNTE, the TSME status has special requirements on enterprises’ number of total employees, annual sales revenue amount, and total assets. The HNTE requires that the core technology of the enterprise’s key products (or services) is specially encouraged by the state and the ratio of income from high-tech related operations against total income is not lower than 60% in the current period, while TSME has no such requirements.
Advanced technology service enterprises (ATSEs)
ATSE status is another core innovation tax policy in China to encourage the provision of information technology outsourcing (ITO), business process outsourcing (BPO), or knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) services to overseas entities.
The CIT rate for a qualified ATSE is 15%.
ATSEs are subject to zero value added tax (VAT) rate for the provision of certain offshore services, which means they can be exempted from the corresponding VAT payment where the simple tax computation method is applicable, or they can enjoy the tax exemption, credit, and refund method where VAT general tax computation method is applicable.
Qualification and criteria
- Be registered in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan);
- Be engaged in one or more categories of advanced technology service businesses listed in the Scopes of Recognized Advanced Technology Service Businesses (for Trial Implementation, hereinafter, the Scope) and adopt advanced technologies or has strong research and development capabilities;
- More than 50% of its staff hold a college degree or above;
- More than 50% of its total revenue at the current year come from the revenue generated from the advanced technology service businesses listed in the Scope; and
- Revenue generated from offshore service outsourcing business is not less than 35% of total revenue at the current year.
Super deduction on R&D expenditure
China also allows for the super deduction of an enterprise’s R&D expenses.
When calculating the CIT taxable income of an enterprise, the R&D cost is usually 100% deductible while the expenses, such as employee education expenses and advertising expenses, are subject to a deduction cap.
R&D activities here refer to processes where an enterprise applies new science and technology knowledge creatively for the purpose of obtaining new science and technology knowledge or carried out systematic activities with specific goals. These activities should aim for substantive improvement of technologies, product (services), and processes.
The expense actually incurred by an enterprise in R&D activities enjoys the below preferential policies:
- For manufacturing enterprises (except tobacco manufacturing), starting from January 1, 2021, if the R&D expenses
- Do not form intangible assets and are included in the current profits and losses, on the basis of actual deduction, an additional 100% of such R&D expenses could be deducted from the taxable income amount; and
- Have formed intangible assets, they can be amortized before CIT at 200% of the actual cost of intangible assets.
- For TSMEs, starting from January 1, 2022, if the R&D expenses
- Do not form intangible assets and are included in the current profits and losses, on the basis of actual deduction, an additional 100% of such R&D expenses could be deducted from the taxable income amount; and
- Have formed intangible assets, they can be amortized before CIT at 200% of the actual cost of intangible assets;
- For other enterprises (except tobacco manufacturing, lodging and catering, wholesale and retail, real estate, leasing and commercial services, and entertainment), starting from January 1, 2023, if the R&D expenses:
- Do not form intangible assets and are included into the current profits and losses, on the basis of actual deduction, an additional 100% of such R&D expenses could be deducted from the taxable income amount; and
- Have formed intangible assets, they can be amortized before CIT at 200% of the actual cost of intangible assets.
Similar to other CIT preferential policies, to enjoy the R&D expenses super deduction policy, enterprises can enjoy the incentive when making tax payment (at the time of pre-payment or final settlement) by self-evaluating if they are qualified and retain relevant documents for future potential inspection of the tax bureau for 10 years.
Tax incentives offered in specific regions
Regions such as the Hainan Free Trade Port (FTP) and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA), are part of China’s economic development strategy, with tax incentives in place to help achieve ambitious development goals.
Other regions, such as the vast western regions, are encouraged due to their lack of geographical and legacy industrial advantages and need policy support to attract investments for economic development.
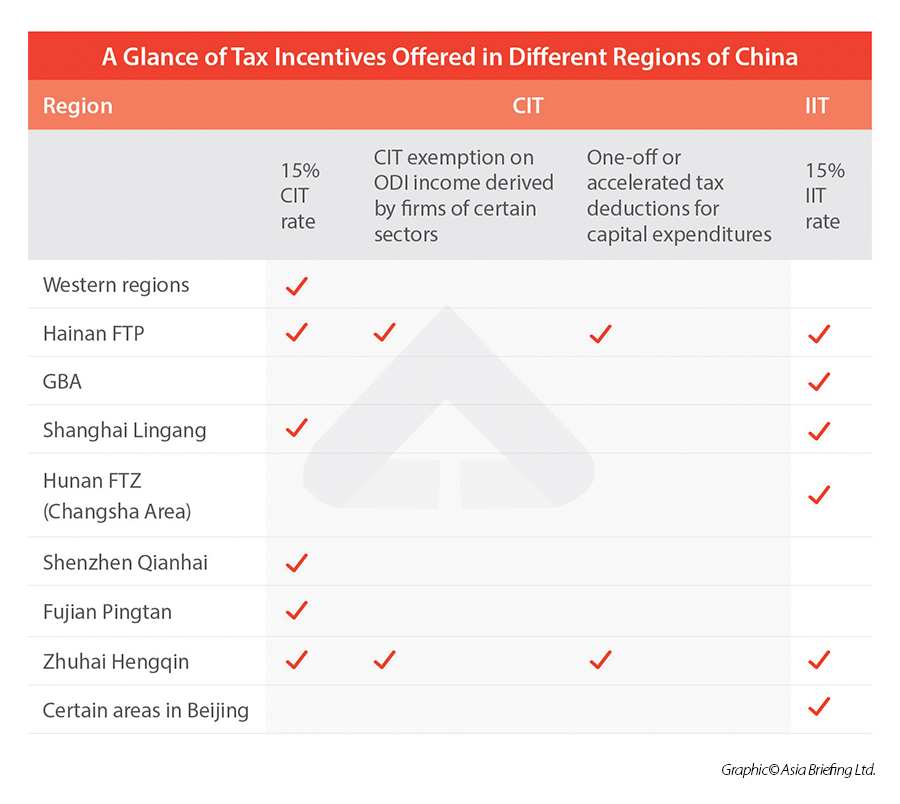
CIT cuts in Western China
Until December 31, 2030, enterprises set up in China’s western regions with their main businesses in encouraged industries of the specific region can enjoy a reduced corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 15%.
The western regions are Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Shaanxi, Gansu, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Yunnan, Qinghai, Tibet, and Xinjiang.
Some underprivileged cities in other provinces – Xiangxi, Enshi, Yanbian, and Ganzhou – may also adopt the same CIT preferential policy.
To be eligible, the enterprise’s main business must fit into the encouraged category of the relevant industry catalogues. Its main business revenue must account for at least 60% of its total business revenue.
|
Chinese Regions Offering Reduced CIT for Encouraged Businesses |
|||
|
Policy |
Region
|
Effective period |
|
|
CIT reduced to 15% |
Western regions
|
2021.1.1-2030.12.31 |
|
|
Hainan FTP |
|
2020.1.1-2024.12.31 (“positive list” management phase) |
|
|
2025-2035 (“negative list” management phase) |
|||
|
Nansha |
|
2022.1.1-2026.12.31 |
|
|
Special economic zones |
Shanghai Lingang |
2020.1.1 (no specific expiration date) |
|
|
Shenzhen Qianhai |
2021.1.1-2025.12.31 |
||
|
Fujian Pingtan |
2021.1.1-2025.12.31 |
||
|
Zhuhai Hengqin |
To be announced |
||
|
“2+3” Tax holiday* |
Xinjiang |
Underprivilaged ares |
2021.1.1-2023.12.31 |
|
5 year tax holiday |
Special economic zones of Kashgar and Khorgos |
|
|
|
* CIT exemption for the first two years (starting from the first income-generating year), and a halved CIT rate (that is, 12.5%) in the subsequent three years. |
|||
Tax incentives in Hainan FTP
China is currently putting considerable effort to transform Hainan island into a world-leading free trade port. To attract businesses and talents, the government has introduced a series of innovative tax relief measures.
|
Type |
Policy |
CIT |
Eligibility criteria |
IIT |
Eligibility criteria |
|
Enterprises registered in Hainan FTP |
15 %
2020.1.1 - 2024.12.31* |
|
Portion of the IIT exceeding 15% of their taxable income can be exempt from 2020.1.1 – 2024.12.31** |
Qualified high-end and urgently needed talents working at Hainan FTP |
|
|
Enterprises of tourism, modern service, and high-tech sectors registered in Hainan FTP |
|
Exempt from paying CIT on income from new overseas direct investment.
2020.1.1 - 2024.12.31 |
|
|
|
|
Venture capital enterprises that are established in Hainan |
|
15 % |
|
Exempt from paying IIT on the portion that exceeds 15 % of their taxable incomes |
Incomes gained in Hainan FTP including comprehensive, business, and talent subsidy income recognized by Hainan Province.
|
|
*From 2025 to 2035, the applicable scope of the lowered CIT rate of 15% will be expanded to benefit all Hainan enterprises (only except those in a “negative list” sector), according to the Overall Plan for the Construction of Hainan FTP released by the State Council. **Hainan has even more IIT relaxation after 2024. From 2025 to 2035, Hainan FTP will limit the IIT brackets on comprehensive income and business income to 3%, 10%, and 15%% (the normal tax brackets are: 3%, 10%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, and 45% for comprehensive income; and 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, and 35% for business income) for certain individuals residing in Hainan. To qualify, the individual must reside in Hainan for no less than 183 days a year. |
|||||
CIT exemption on overseas direct investment income
Additionally, to enjoy the tax exemption, the foreign jurisdiction, where the overseas branch is located or investment is made, must impose a statutory income tax of five% or more.
Accelerated tax deductions for eligible capital expenditures
Furthermore, Hainan-registered enterprises are allowed to accelerate the pre-tax deduction of the cost of fixed assets (excluding building) or intangible assets that are acquired between January 1, 2020 and December 31, 2024.
- For assets with a unit value no more than RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million), a one-off pre-tax deduction is allowed; and
- For assets with a unit value of more than RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million), accelerated depreciation or amortization is allowed.
Tax incentives in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao GBA
IIT incentives
In GBA, foreign high-end talents and urgently needed talents working at the nine mainland cities – namely Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Foshan, Huizhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, and Zhaoqing – can apply for a financial subsidy to lower their IIT burdens from January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2023. The subsidy amounts to the portion of the IIT paid by the qualified talent that exceeds 15% of one’s taxable income, according to Cai Shui [2019] No.31. Read more here.
|
IIT Incentives – Hainan vs GBA :Preferential IIT Rates in Specific Regions of China |
||
|
Area |
Hainan FTP |
Nine GBA cities |
|
IIT rate |
Comprehensive income, business income, and talent subsidy income recognized by the Hainan government |
Comprehensive income, business income, and subsidy income from selected talent programs and talent projects |
|
15% (2020.1.1-2024.12.31) |
15% (2019.1.1-2023.12.31) |
|
|
3%, 10%, 15% (2025-2035) |
- |
|
|
Scope of eligible talents |
Before 2025: eligible foreign and domestic high-end talents and talents in short supply. Before 2035: eligible individuals who reside in Hainan FTP for more than 183 days in a tax year. |
Eligible overseas talents high-end talents and talents in short supply. |
|
Application process |
No need to apply. The portion of the IIT that exceeds 15% of the taxable income paid last year will be refunded to the talent after annual final settlement of IIT. |
Need to apply during a specific period each year. The portion of the IIT that exceeds 15% of the taxable income paid last year will be returned to the talent as a subsidy after the application is made. |
| * In addition to Hainan FTP and GBA, Shanghai Lingang New Area, Guangdong-Macao ICZ (Zhuhai Hengqin), and certain areas in Beijing also implemented or will implement similar IIT incentives. Detailed implementation rules are yet to be announced. | ||
The IIT incentives in Hainan FTP and in GBA both aim to lower the actual income tax burden of qualified talents to 15% of their taxable income. Besides, in both policies, taxable income refers to the individual’s comprehensive income, business income, and recognized subsidy income (investment or asset transfer income is not covered).
However, there are also some differences:
- Hainan’s IIT policy applies to both foreign and domestic talents, while GBA’s IIT incentive is only applicable to foreign talents (including residents of Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan);
- Eligibility criteria for Hainan’s IIT incentives considers social security contributions, proof of labor relationship, minimum annual income (for “high-end talents”), and the talent catalogue (for “talents in short supply”). In the GBA, qualification criteria vary from city to city. In addition to the basic requirements, foreign talents also need to satisfy additional criteria in their city (such as the city’s catalogues of high-end talents and talents in short supply, the minimum working days/annual income requirements, etc.); and
- To enjoy the IIT relief, GBA talents need to file applications during a specific period each year. The excess portion of the IIT paid last year will be returned to the talent this year as a subsidy after the application is successful. However, Hainan provides a more streamlined process. Overpaid tax can be refunded to the talent immediately after the talent completes the annual final settlement of IIT.
Notably, some other special economic zones, including Lingang New Area of Shanghai Free Trade Zone (FTZ), Guangdong-Macao Intensive Cooperation Zone (also known as Zhuhai Hengqin area), and Hunan FTZ Changsha Area adopt similar IIT policies.
VAT incentives in the GBA
|
VAT incentives in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao GBA |
||||
|
Type |
Incentives |
Policy |
Validity period |
Eligibility criteria |
|
Insurance companies |
Vat exemption & tax refund at port of departure |
|
|
|
|
Insurance enterprises registered in Guangzhou from enterprises registered in Nansha Area of Guangdong FTZ |
VAT exemption |
|
October 1, 2020 to December 31, 2023 |
Income should be derived from insurance premium for international shipping |
|
Containerized cargos shipped abroad from the designated 37 ports of shipment |
Eligible for export tax rebate at the port of the shipment
|
|
|
The cargos should pass through Nansha Bonded Port of Guangzhou & Qianhai Bonded Port of Shenzhen (the place of departure) by qualified export enterprises with qualified transportation enterprises as the carriers. |
Tax incentives in Shanghai Lingang New Area
| CIT Incentive | Eligibility criteria | Validity period | Policy |
| 15% | Business must be in – integrated circuits (IC), artificial intelligence (AI), biomedicine, or civil aviation. Enterprise must engage in substantive production and R&D activities in a sector listed in the Catalogue of Key Fields and Core Links of Lingang New Area. | For 5 years since its date of establishment | Cai Shui [2020] No.38 |
| IIT incentives | Eligibility criteria |
| 15% | For foreign high-end and needed talents |
| VAT incentives | Eligibility criteria | Policy |
| Exempt from VAT 2021.1.1 - 2024.12.31 | Enterprises should be registered in Yangshan Special Comprehensive Bonded Zone (CBZ) of Lingang New Area: Income should be derived from providing transportation services, handling services, and warehouse services within the zone. | Cai Shui [2021] No.3 |
Tax incentives in Shenzhen Qianhai
|
CIT incentives |
Policy |
Validity period |
Eligibility criteria |
|
15 % |
January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2025 |
Qualified enterprises engaged in encouraged business activities in Qianhai Shenzhen-Hong Kong Modern Service Industry Cooperation Zone |
Tax incentives in Fujian Pingtan
|
CIT incentives |
Policy |
Validity period |
Eligibility criteria |
|
15% |
Cai Shui [2021] No.29 |
January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2025 |
Qualified enterprises engaged in encouraged business activities in Pingtan Comprehensive Experiment Zone of Fujian FTZ |
Tax incentives in Zhuhai Hengqin (Guangdong-Macao ICZ)
The State Council rolled out a masterplan for the construction of Guangdong-Macao Intensive Cooperation Zone (ICZ), which contains a series of favorable tax policies.
|
CIT incentives |
IIT incentives |
Eligibility for IIT incentives |
|
15%
CIT will also be exempt on the newly added earnings from overseas direct investment into the tourism, modern services, and high technology businesses set up in the Cooperation Zone. |
Exemption from paying the portion of income tax that exceeds 15% of their taxable income |
Overseas and domestic high-end talents and shortly needed talents |
Capital expenditure of businesses that meets the criteria will be allowed a one-off deduction before tax for the taxation period in which the expenditure occurred or accelerated depreciation and amortization.
|
Encouraged Industries in Certain Development Zones of China |
|||
|
Shanghai Lingang 23 industry sectors under four categories |
Shenzhen Qianhai 30 industry sectors under five categories |
Zhuhai Hengqin Catalogue to be announced |
Fujian Pingtan 146 industry sectors under five categories |
|
|
|
|
Beijing IIT incentives
Eligible overseas high-end talents working in certain areas of Beijing will be able to enjoy preferential IIT policy, according to the State Council. The detailed implementation measures are yet to be announced.
Tax incentives in Beijing Zhongguancun
| CIT incentives on income from qualified technology transfer | ||
| Type | CIT incentive | Policy |
| Resident enterprises registered in Beijing Zhongguancun National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone | Exemption on income from qualified technology transfer not exceeding RMB 20 million (approx. US$3.1 million); and CIT on income from qualified technology transfer exceeding RMB 20 million (approx. US$3.1 million) can be halved. | Cai Shui [2020] No.61 |
CIT reduction for venture capital enterprises
Furthermore, according to Cai Shui [2020] No.63, effective from January 1, 2020, for qualified corporate venture capital enterprises (CVCE) in the Demonstration Zone:
- If the gains on the transfer of equity, which has been held for not less than three years, exceeds 50 percent of the total gains on the transfer of equity in a given tax year, a 50 percent exemption for CIT based on the shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end is allowed (CIT Exemption = Shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end x CIT liability for year ÷ 2); and
- If the gains on the transfer of equity, which has been held for not less than five years, exceeds 50 percent of the total gains on the transfer of equity that year, a 100 percent exemption for CIT based on the shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end is allowed (CIT Exemption = Shareholding ratio of individual shareholders at year-end x CIT liability for year).
Tax incentives for small businesses
CIT incentives for small and low-profit enterprises
All types of SLPEs in China are able to enjoy a reduced corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 20 percent in combination with a reduction of their tax base.
Specifically, SLPEs are subject to:
|
Corporate Income Tax Cuts for Small And Low-Profit Enterprises |
||||
| Annual taxable income(ATI) | Tax base | CIT rate | Effective CIT rate | Effective period |
| The portion below RMB 1 million | ATI*12.5% | 20% | 5% | 2023.1.1-2024.12.31 |
| The portion between RMB 1 million and RMB 3 million | 2022.1.1-2024.12.31 | |||
SLPEs refer to enterprises engaged in non-restrictive and non-prohibited businesses that meet the following three conditions:
- Annual taxable income not exceeding RMB 3 million (approx. US$458,500);
- Number of employees not exceeding 300; and
- Total asset value not exceeding RMB 50 million (approx. US$7.7 million)
As the SLPE evaluation is carried out at the entity level (instead of at the group level), small subsidiaries of foreign multinational enterprises (MNEs) can also benefit from these CIT cuts..
VAT incentives for small-scale taxpayers
|
VAT incentives for small scale taxpayers |
|||
|
Monthly sales amount |
Quarterly sale amount |
VAT incentives |
Surtaxes** & other reduction
|
|
Under RMB 100,000 (approx. US$14,740) |
Under RMB 300,000 (approx. US$44,220) |
Exempt from VAT 2023.1.1 – 2023.12.31 |
Exempt from education surcharge, local education surcharge, and water conservancy construction fund |
|
Over RMB 150,000 but the sale should be < RMB 150,000 when excluding real estate sales occurring in the current period. |
|
Exempt from VAT*
2023.1.1 – 2023.12.31 |
|
|
Over RMB 100,000 but the sale should be < RMB 100,000 when excluding real estate sales occurring in the current period. |
|
Exempt from VAT*
2023.1.1 – 2023.12.31 |
|
|
*On the sale of goods, labor services, services, and intangible assets. ** China’s national and local education surcharges, in addition to Urban maintenance and construction tax (UMCT), are calculated based on a taxpayer’s actual payment of VAT and consumption tax. Small-scale taxpayers can choose to waive the VAT exemption incentive and instead issue special VAT invoices for a specific sale. |
|||
Reduced VAT rates
During the period between January 1, 2023, and December 31, 2023, small-scale taxpayers that are subject to a VAT levy rate of 3% can enjoy a reduced levy rate of 1%. The VAT items that are subject to a 3% VAT prepayment rate shall enjoy a reduced prepayment rate of 1%.
Small-scale taxpayers can choose to waive the VAT reduction incentive and instead issue special VAT invoices for a specific sale.
Additional VAT reduction policy
| Additional VAT Deduction Policy, 2023 | |
| Category | VAT rate |
| Taxpayers in lifestyle services | 10 percent (January 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023) |
| Taxpayers in production-oriented services | 5 percent (January 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023) |
Other tax reduction
Local governments are granted authority to reduce levying of six types of taxes and two fees on small-scale taxpayers within the tax base of 50% during the period between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2024.
The “six taxes” are:
- UMCT;
- Property tax;
- Urban and township land use tax;
- Stamp tax (excluding securities transaction stamp tax);
- Farmland occupation tax; and
- Resource tax.
The “two fees” are:
- Education Surcharge (ES); and
- Local Education Surcharge (LES).
IIT incentives for small business owners
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2022, individually owned businesses, sole proprietorships, and partnership enterprises can enjoy some individual income tax (IIT) relief.
For the portion of an individually owned business’ income from a business operation that does not exceed RMB 1 million, the business is entitled to a 50% reduction of IIT on the basis of the prevailing incentives.
From April 1, 2021, individually owned businesses, sole proprietorship enterprises, partnership enterprises, and individuals will no longer be required to pre-pay IIT at the time of issuance of cargo transport VAT invoices on behalf.
Tax measures to lower financing costs of small businesses
To help small and micro enterprise raise funds, China exempts financial institutions from paying VAT on their interest income derived from small loans to farmers, small enterprises, micro enterprises, and individually owned businesses. Besides, loan contracts signed between small or micro enterprises and financial institutions are exempt from stamp tax.
Both measures are effective until December 31, 2023.
China’s VAT Rebates Policy in 2022
In the face of growing economic pressure from COVD-19 containment measures, high operational costs, and global logistics and macroeconomic turmoil, China has released a slate of tax relief measures to ease the burden on small businesses and companies in key industries.
The government has pledged around RMB 1.5 trillion (approx. US$ 238 billion) of large-scale tax rebates on VAT credit over the course of 2022. To increase the efficiency and effectiveness of the rebates, the government also issued directives to speed up the payment of refunds for certain businesses.
Foreign businesses and their subsidiaries that fall under the categories of eligible companies eligible can apply for a full refund of incremental VAT credit on a monthly basis and a one-off refund of their remaining VAT credit accordingly.
Note: For the purpose of this section, VAT rebates and VAT credit refunds are mutually used to refer to the VAT relief provided in China.
Background
What are VAT rebates?
VAT, or value-added tax, is one of the major indirect taxes levied in China. Rates range from six to 13% for general VAT taxpayers. VAT credit is the overpaid input VAT at the end of each taxable period when the input VAT exceeds the output VAT.
Since April 2019, when China began deepening VAT reform, qualified taxpayers in all industries were allowed to apply for uncredited VAT refunds in the current taxable period. Starting in June 2019, qualified taxpayers in the advanced manufacturing industry were able to enjoy a similar but more relaxed policy.
Now, the VAT credit refund policy will be applied even more broadly. The full refund of incremental VAT credit on a monthly basis, which was previously only available to companies in the advanced manufacturing industry, is now available to micro and small firms in all industries and qualified enterprises in another twelve industries.
Moreover, qualified enterprises will enjoy a one-off refund of their remaining VAT credit in turn following a decided calendar.
Expansion of VAT rebates in 2022
In the 2022 Government Work Report released on March 5, the government announced that an estimated RMB 2.5 trillion would be handed out in tax rebates and cuts in 2022, of which RMB 1.5 trillion would be earmarked for tax rebates specifically. All of these funds would go directly to eligible companies, the report stated.
RMB 1 trillion of the funds will be provided as VAT refunds to micro and small enterprises (MSEs) and sole proprietorships in all industries.
The VAT relief is a key measure for stabilizing development, stabilizing market entities, and ensuring employment and also serves to conserve tax sources and improve the VAT system, according to the readout.
In addition to MSEs and sole proprietorships, the remaining tax credits for eligible companies of all sizes in certain industries will be refunded in full between July 1 and the end of the year.
On March 22, 2021, the Ministry of Finance (MOF) released an announcement [Announcement (2022) No. 14] that provided more details on the expansion of the VAT credit refunds for MSEs and qualified companies in six specific industries, clarifying the eligibility criteria for companies, how to assess the number of VAT credits that can be refunded and other definitions.
On June 7, the MOF and STA issued another notice [Announcement (2022) No. 21], further expanding the scope of companies eligible for VAT credit refunds to include those in an additional seven industries.
Who can apply for VAT rebates?
Qualified micro and small firms in all industries and all qualified enterprises in 13 industries can apply for VAT rebates.
What are micro and small firms?
Micro, small, medium, and large companies are specific legal designations in China, as stipulated in regulatory documents, such as the Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Classification Standard Regulations.
The specific parameters for company size depend on the industry in which the company is operating. Below are some of the size parameters for various industries. Note that large companies are defined as companies with operating income, assets, and staff numbers above the designated threshold for medium-sized companies in each industry.
|
Company Size Classification by Industry |
|||
|
Sector |
Micro |
Small |
Medium |
|
Industry (including mining, manufacturing, electricity, heat, gas, and water production and supply) |
|
|
|
|
Construction |
|
|
|
|
Retail |
|
|
|
|
Transport and logistics |
|
|
|
|
Catering |
|
|
|
|
Information transmission |
|
|
|
|
Software and information technology |
|
|
|
|
Real estate |
|
|
|
|
Source: Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Classification Standard Regulations Note: The above list is not exhaustive. |
|||
Total assets are determined according to the taxpayer’s end-of-year value in the previous fiscal year. Operating income is determined according to the taxpayer’s VAT sales in the previous fiscal year. If the duration of VAT sales amounts to less than one fiscal year, it is calculated according to the following formula:
VAT sales (year) = VAT sales during the actual duration of the enterprise in the previous fiscal year / number of months of the actual duration of the enterprise × 12
The STA announcement released on June 7, 2022 also further clarified that the industry that an MSE belongs to is determined by looking at which industry accounted for the company’s highest proportion of its total VAT sales in the previous fiscal year. The industry is determined as per the definition in the Industrial Classification for National Economic Activities (PDF) (link in Chinese). This requirement is effective as of June 7, 2022.
Which industries are eligible for VAT rebates?
As stipulated in the STA Announcement (2022) No. 14 released on March 22 2022, the VAT rebate policy has been extended to include all eligible companies in the following six industries:
- Manufacturing;
- Scientific R&D and technology services;
- Electricity, heating, gas, and water production and supply;
- Software and information technology services; and
- Ecological protection and environmental governance; and Transport, logistics, warehousing, and postal.
The STA Announcement (2022) No. 21 released on June 7, 2022, further expanded this policy to cover companies in an additional seven industries, which are:
- Wholesale and retail;
- Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery;
- Hospitality and catering;
- Residence, repairs, and other services;
- Education;
- Healthcare and social work; and
- Culture, sports, and entertainment.
To qualify for VAT rebates, VAT sales related to one of the 13 industries listed above must account for over 50% of the company’s total VAT sales. The 13 industries are determined per the legal definition in the Industrial Classification for National Economic Activities.
The proportion of VAT sales is calculated and determined based on the company’s sales for 12 consecutive months before applying for the refund. If the company has been operating for less than 12 months but more than three months prior to applying for the refund, then the VAT sales are calculated and determined based on the sales during the actual operating period.
Which companies are “qualified”?
Qualified enterprises refer to companies that meet all of the following criteria:
- Have an A or B tax credit rating;
- Have not fraudulently obtained tax refunds for remaining credits, fraudulently obtained export tax refunds, or falsely issued special VAT invoices in the 36 months prior to the application;
- Have not been punished twice or more by the tax authority for tax evasion within 36 months of applying for the tax refund; and
- Have not enjoyed the preferential policy of “refund upon payment and return (refund) after payment” since April 1, 2019.
All MSEs and companies in the 13 industries must meet the above criteria to qualify for the VAT credit rebates.
Timeline for applying for VAT rebates
Micro, small enterprises, and sole proprietorships
Qualified MSEs can apply to the competent tax authority for a refund of incremental tax credits on a monthly basis starting from the tax filing period in April 2022.
The timeline for application of the one-time refund of the remaining tax credit is as follows:
- From the tax filing period in April 2022, eligible micro-enterprises could apply for a one-time refund of the remaining tax credits to the competent tax authority; and
- From the tax filing period in May 2022, eligible small enterprises can apply for a one-time refund of the remaining tax credits to the competent tax authority.
The MOF announcement released on March 21 stated that VAT refunds for MSEs should be paid by April 30 and June 30 respectively, on the basis of voluntary applications by the companies.
Companies in the 13 industries
Companies in the 13 industries listed above are eligible for a full refund of incremental VAT credits on a monthly basis as well as a one-time refund of the remaining tax credits.
Starting from the tax filing period in April 2022, enterprises in the first list of six industries can apply for refunds of incremental tax credits to the competent tax authority.
Moreover, medium and large enterprises in these six industries can also apply for a one-time refund of the remaining tax credits (micro and small in the six industries are also eligible for this by default under the conditions for MSEs described above). The timeline for application is as follows:
- Starting from the tax filing period in May 2022, qualified medium-sized enterprises in the six industries can apply to the competent tax authority for a one-time refund of the remaining tax credits; and
- From the tax declaration period in June 2022, qualified large enterprises in the six industries can apply for a one-time refund of the remaining tax credit to the competent tax authority.
According to the April 17, 2022, announcement and the May 17, 2022, announcement of the MOF, the remaining tax credits will be refunded to medium-sized and large enterprises in the first list of six industries before June 30, 2022, based on a voluntary application by taxpayers.
Meanwhile, companies in the second list of seven industries can apply for both the refund of incremental VAT credits and one-time refund of remaining VAT credits from July 1, 2022. The announcement did not specify a deadline for the refund of VAT credits for companies in these seven industries.
How is the VAT rebate amount calculated?
Defining incremental and remaining VAT credit
The MOF announcement released on March 22, 2022, clarified that both incremental input VAT credit and the remaining VAT credits can be refunded under the scheme.
The incremental VAT credit is determined by distinguishing between the two following situations:
- Before a taxpayer obtains a one-time refund of the remaining VAT credit, the incremental VAT credit is the newly increased tax credit at the end of the current period compared with March 31, 2019; and
- After the taxpayer obtains a one-off tax refund for the remaining VAT credit, the incremental tax credit shall be the end-of-period tax credit.
The remaining VAT credit is determined according to the following circumstances:
- Before a taxpayer obtains a one-time refund of the remaining VAT credit, if the amount of VAT credit retained at the end of the current period is more or equal to the amount of tax credit retained at the end of March 31, 2019, the amount of the remaining VAT credit is the same as the amount of VAT credit retained at the end of March 31, 2019;
- If the amount of VAT credit retained at the end of the current period is less than the amount of tax credit retained at the end of March 31, 2019, then the amount of remaining VAT credit is the same as the amount of tax credit retained at the end of the current period; and
- After the taxpayer obtains a one-off tax refund for the remaining VAT credit, the remaining VAT credit will be zero.
Calculating VAT credit amount
To calculate the amount of VAT credits that can be refunded, companies can follow the following formula:
Incremental tax credits allowed to be refunded = incremental tax credits × input VAT ratio × 100%
Remaining tax credits allowed to be refunded = remaining tax credits × input VAT ratio × 100%
Input VAT ratio refers to the ratio of VAT amount indicated on relevant VAT invoices (or fapiao) which have been credited from April 2019 up until the tax period prior to the application for tax refund, to the total credited input VAT in the same period. Relevant VAT invoices here include:
- Special VAT invoices (including fully digitized electronic invoices with the words “special VAT invoices” and unified tax-controlled motor vehicle sales invoices;
- General electronic invoices for toll road VAT;
- Customs Import VAT Special Payment Note; and
- Receipts of tax payment certificate.
According to STA Announcement [2022] No. 4, when calculating the input VAT ratio, the input VAT transferred out by a taxpayer – as required from April 2019 up until the tax period before the application for tax refund is filed – does not need to be deducted from the VAT amount indicated on any relevant VAT invoices that have been deducted.
How to apply for VAT refunds
To apply for a VAT refund, companies must first complete the filing and payment of VAT for the current period before they can apply for the VAT return. To apply, companies must submit the Tax Refund (Credit) Application Form (PDF) (link in Chinese) through the Electronic Taxation Bureau (link in Chinese) or to the Tax Service Office.
Taxpayers that have already taken advantage of the preferential policy of “refund upon payment and return (refund) after payment” since April 2019 can still apply for a refund of the remaining VAT credits – if they first return the previously refunded VAT. The full amount must be repaid before October 31, 2022. This can be done by submitting the Application Form for the Return of Excess Input VAT Credits through the Electronic Taxation Bureau (link in Chinese) or to the Tax Service Office.
The other side of the coin: Intensifying the crackdown on tax fraud
While China substantially expands and accelerates the implementation of the VAT rebate policy, it is also stepping up the crackdown on fraudulent and criminal behavior.
From April 1 to May 10, 2022, the public security and tax authorities launched investigations into more than 1,800 enterprises suspected of defrauding tax refunds and confirmed that 448 enterprises have obtained tax refunds illegally or fraudulently, involving RMB 822 million in tax refunds. 74 cases of fraudulent tax refunds have been publicly exposed.
On May 17, 2022, the STA and other five regulators jointly released the Circular on Severely Cracking Down on Illegal and Criminal Acts of Defrauding Value-added Tax (VAT) Credit Refunds, which further demonstrated China’s determination in combating fraud in VAT rebate procedures.
In cases where a company has fraudulently obtained the remaining tax refund by falsely increasing items, making false declarations, or other deceptive means, the tax authority will recover the fraudulently obtained tax refund, and deal with it in accordance with the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Administration of Tax Collection, the Administrative Penalty Law of the People’s Republic of China, and other relevant regulations.
Although the laws do not stipulate a specific punishment or fine for VAT credit refund fraud, typical cases released by the STA show that companies found to have engaged in fraudulent behavior to obtain VAT refunds have been recommended fines of up to two times the total amount of tax fraudulently obtained.
It is therefore extremely important that companies adhere to China’s tax laws and follow application guidelines closely to ensure that they do not increase the amount of input VAT on the application, whether on purpose or by accident.
Other general incentives
Other projects are also entitled to CIT preferential policies that are mentioned below. Investors should consult tax professionals in China for information on the most up-to-date tax incentives available to them.
- CIT incentives for hiring disabled employees - An additional 100% deduction of salaries paid to disabled employees based on actual deduction;
- Tax reduction for enterprises investing in west China - Qualified enterprises making investments to encouraged industries in the west China region can enjoy a reduced CIT rate of 15% before December 31, 2030, upon approval by the relevant tax office. The western region includes, but is not limited to, Chongqing Municipality, Sichuan Province, Yunnan Province, Guizhou Province, Shanxi Province, and Ningxia Province;
- Income derived from eligible technology transfers - Income as obtained by a resident enterprise through transferring eligible technology could be exempted from CIT for the part not exceeding RMB 5 million, and the excess shall be subject to 50% CIT reduction; and
- Tax reduction for enterprises investing in seed-stage or start-up technology enterprises - Qualified enterprises making investment to seed-stage or start-up technology enterprises in pilot cities--Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanghai, Guangdong, Anhui, Sichuan, Wuhan, Xi’an, Shenyang and Suzhou Industrial Zone, can deduct 70% of the investment amount from the taxable income from January 1, 2017. Investments made two years prior to the effective date could also apply this benefit. This incentive has been expanded nationwide since January 1, 2018.













