In this city profile, we highlight key factors that make investing in Dongguan a viable option for foreign enterprises seeking to set up in China. The city's history traces a journey from being a cheap export-oriented manufacturing base to developing high-tech strengths. In many ways, the story of Dongguan reflects the transformation of the modern Chinese economy.
Often known as “factory to the world”, the Dongguan of old was China’s biggest export hub. Since this humble beginning – churning out and exporting cheap products – Dongguan is now looking to transit into a smart manufacturing base, focused on high-tech robotics and automated equipment.
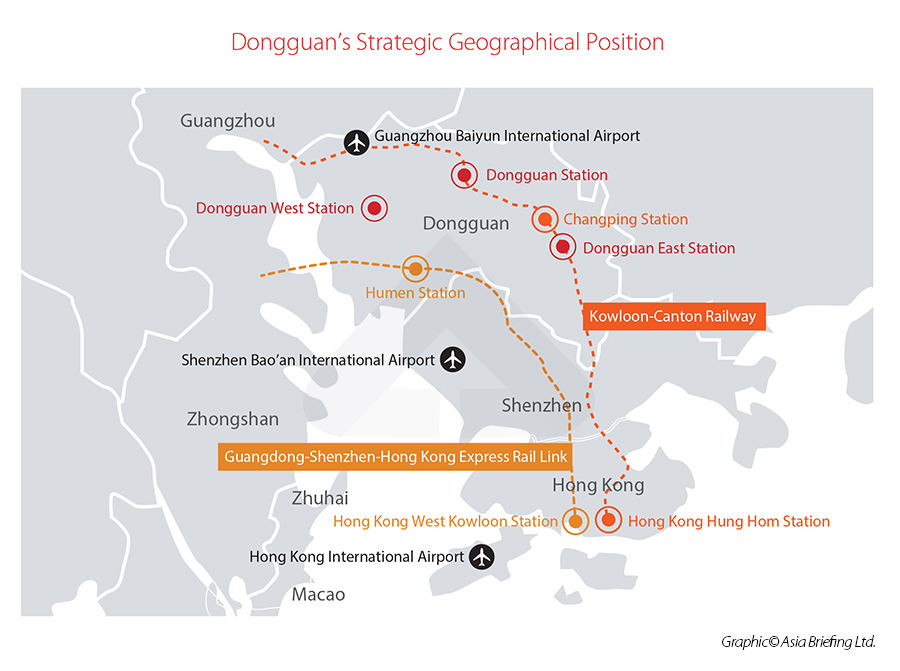
Situated right at the center of the urban agglomeration of the Pearl River Delta region, Dongguan occupies a strategic location. The city falls right between Shenzhen and Guangzhou, benefiting off of a spillover effect from the two megacities in Guangdong province. For example, in 2018, the Chinese tech giant Huawei Technologies, headquartered in Shenzhen, opened a high-profile research lab Huawei's Ox Horn Campus in Dongguan, which accommodates about 25,000 employees, and this was followed by the movement of a number of upstream and downstream companies.
Given the robust infrastructure of the Greater Bay Area (GBA), Dongguan is easily accessible. Three of the busiest international airports in southern China – Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport, Shenzhen Bao 'an International Airport, and Hong Kong International Airport -- are within an hour from Dongguan. The distance from Dongguan to Hong Kong (about 140 kilometers) is covered by a 30-minutes ride through the Guangdong-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link.
Moreover, Dongguan is at the center of the Guangzhou-Shenzhen Technology Innovation Corridor, the most important economic belt in the GBA that connects Guangzhou, Dongguan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong to accumulate the best innovation resources from the four cities. The city is poised to profit from the rise of China's tech industry and booming domestic consumption.
To transform itself into an advanced manufacturing stronghold, Dongguan has lavished money on R&D. In 2019, R&D expenses accounted for 3.1 percent of the Dongguan’s economy output, the second highest in Guangdong province, only behind Shenzhen. Currently, Dongguan is home to China Spallation Neutron Source (CSNS), one of the world’s four major spallation neutron sources (SNS), which can provide pulsed neutron beams for scientific research. It also houses more than 4,000 national high-tech enterprises and 31 provincial innovative scientific research teams.
More recently, in March 2021, it was announced that the Greater Bay Area (GBA) University will build two campuses in Dongguan over a six-year period (2020-2026) – one campus will be in the Songshan Lake High-Tech Zone and one in Binhaiwan New Area. The university is designed to become a leading world-class institution, nurturing high-end scientific and technological talents to boost the GBA’s development.
Investing in Dongguan: Economic profile and leading industries
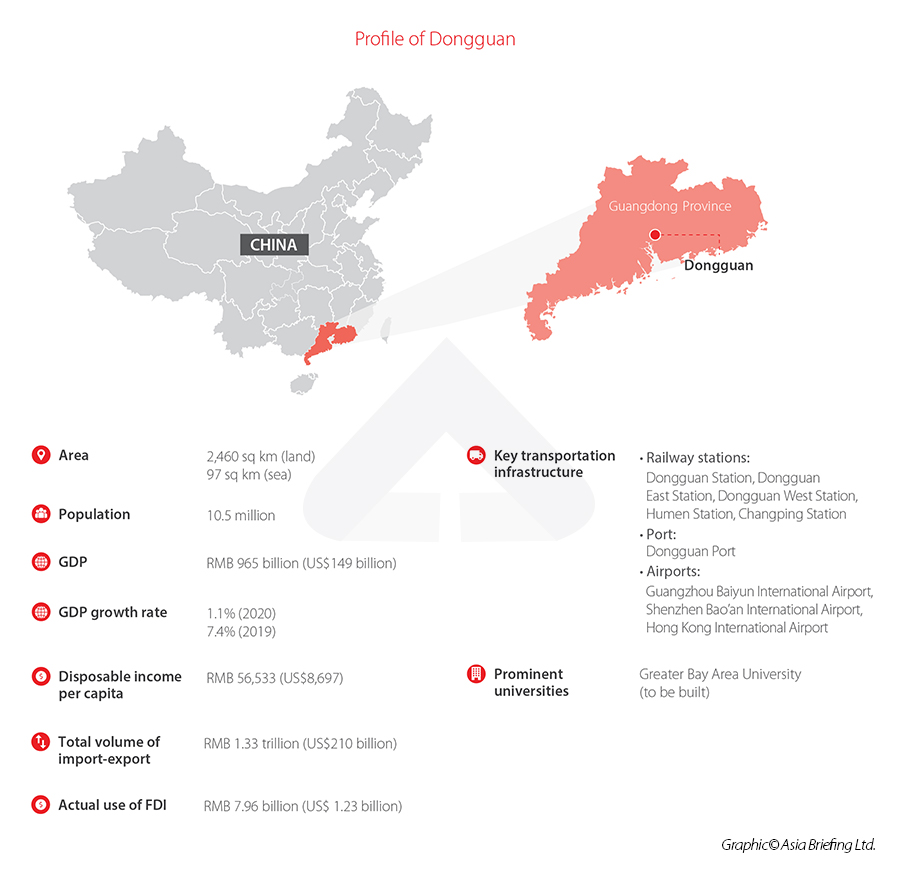
Dongguan is the fifth largest city in the GBA in terms of GDP (RMB 956 billion/US$149 billion), after Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Hong Kong, and Foshan. It is getting close to joining the “trillion yuan club” with the first four front runners.Manufacturing is the pillar that makes up almost 54 percent of Dongguan’s GDP. More specifically, export-oriented manufacturing is the main driver. In 2020, Dongguan accounted for 19 percent of the total exports of Guangdong province in value terms, second only to Shenzhen. Of Dongguan’s exported goods, mechanical and electrical products accounted for 75.6 percent.
So far, Dongguan has lured over 170,000 industrial enterprises. With big Chinese smartphone makers, including Huawei, Vivo, and Oppo, opening factories here in 2019, Dongguan produced one-quarter of the world’s smartphones shipments.
The boom in emerging Chinese tech manufacturers has also given Dongguan’s robotics industry a boost. It was home to about 400 companies focused on producing robots and automated equipment last year, according to official data. They employed more than 55,000 people, with output valued at RMB 35 billion (US$5.4 billion).
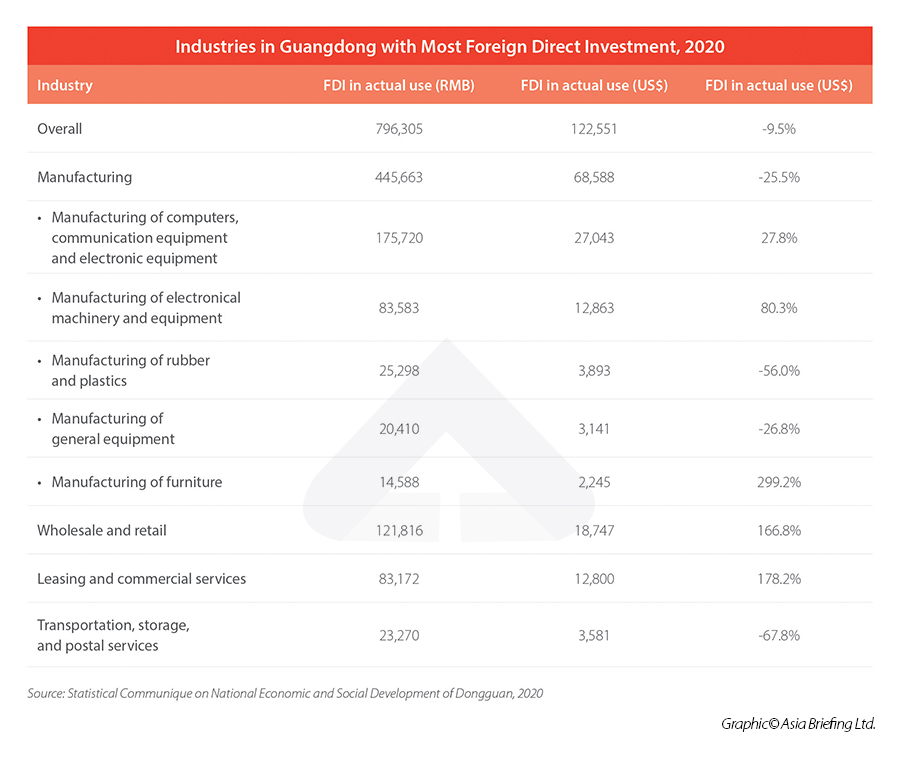
As for foreign direct investment (FDI), over the same period, the city utilized some RMB 7.96 billion (US$1.23 billion) of overseas capital, with 56 percent of that invested in the manufacturing sector. Over 10,000 foreign invested enterprises have set up base here.
Dongguan has five leading industries, four specialty industries, and 10 strategic emerging industries.
The five leading industries are electronic information manufacturing; electrical machinery and equipment manufacturing; textile, clothing, and shoes; food and beverage manufacturing; and paper and paper products. In 2020, the total value‑added industrial output of the enterprises (above a designated scale) in these five sectors was RMB 280.7 billion (US$43.24 billion), down 2.1 percent on the previous year.
The specialty industries are toys, stationery, and sports supplies; furniture making; chemical products; and packaging. Cumulatively, they delivered an output worth RMB 36.9 billion (US$5.68 billion) in 2020, up 0.6 percent year-on-year.
The 10 strategic emerging industries include next-generation information technology, artificial intelligence (AI), intelligent terminals, industrial robot, high-end intelligent manufacturing equipment, advanced materials, new energy vehicles, high-performance battery, biomedicine, and high-end medical equipment.
Among them, the high-end intelligent manufacturing equipment, intelligent terminals, and next-generation information technology sectors have incubated the most enterprises above designated scale. (In China, industrial enterprises above designated size refer to those with annual main business income of more than RMB 20 million.)
In the services sector, Dongguan plans to promote the development of high-end services in software information, scientific research, e-commerce logistics, cultural creativity, certification testing, human resources, and other fields.
To boost e-commerce logistics, the city said it would invest more in cross-border logistics, cold chain logistics, supply chain logistics. To achieve smart logistics, the government will support the application of cloud computing, Internet of things, and other technologies for intelligent logistics management, to create a professional logistics public information platform.
Operating costs in Dongguan
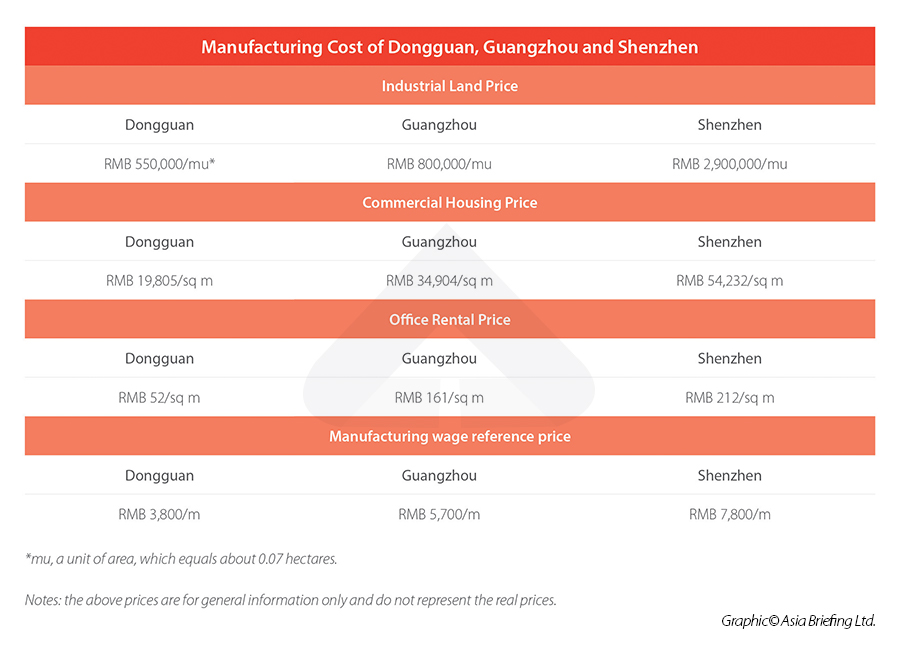
Dongguan boasts that it has a “first-tier city’s geographical position” but “second-tier city’s cost of living and production”. According to estimates from Dongguan’s municipal government, compared with the neighboring Shenzhen and Guangzhou, the city’s industrial land prices can be 30 percent to 80 percent cheaper. Office rents in Dongguan can be as low as 24 percent of those in Shenzhen and 32 percent of those in Guangzhou.Dongguan’s key investment areas
Songshan Lake High-Tech Industrial Development Zone
Dongguan’s Songshan Lake Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone, where Huawei has built a smart manufacturing hub, serves as a new engine to drive Dongguan’s high-tech economic transition and innovative capacity.The zone is close to Hong Kong and Shenzhen in the south and Guangzhou in the north, sitting in the center of the Guangzhou-Shenzhen Technology Innovation Corridor. At present, it ranks 21st in the comprehensive ranking of China’s national high-tech zones.
Dongguan Songshan Lake Hi-Tech Zone focuses on high-end electronic information, biopharmaceuticals, robotics, new energy, and modern services industries. By far, it has attracted 1400 national high-tech enterprises and 200 R&D institutions.
As an eco-friendly industrial development zone, it covers a planning area of more than 90 square kilometers (including lake surface area of eight square kilometers, wetland area of 6.5 square kilometers, and ecological green land area of 14 square kilometers) and has a green coverage ratio of over 60 percent.
City University of Hong Kong (Dongguan) and the GBA University (Songshan Lake Campus) are settled in Songshan Lake Science City, which is scheduled to start construction in 2021.
Binhaiwan New Area
The Binhaiwan New Area lies right on the strategic corridor between the northern districts of Shenzhen and the special economic zone in Nansha on the southern fringes of Guangzhou.With a land area of 83.2 square kilometers (60 square kilometers are available for construction), this emerging region is under development, which is in full swing. Among the development projects are the GBA University’s Binhaiwan Campus, which is planned on Weiyuan Island to serve as an innovation cluster in the area.
The masterplan for the construction of Binhaiwan New Area lists 28 key infrastructure and facility projects, including some environmentally sustainable projects like a low-speed transportation system like bicycle tracks and pedestrian paths and the “three green hearts” – the Weiyuan Island Forest Park, Binhaiwan Bay Central Agricultural Park, and Modie River Wetland Park.
“Smart City” applications will also be adopted, including smart streetlights, smart parking lots, smart driving, and smart logistics.
Another focus of the masterplan is cooperation with Hong Kong and Macao. The Dongguan government plans to build a 1500-acre Youth Innovation Town in the area, deepening ties with the two special administration regions (SARs) in talent exchange, culture, education, healthcare, youth entrepreneurship, and finance. The Youth Innovation Town is expected to attract 3,000 young talents by 2025 and 30,000 in 2035.
The Binhaiwan New Area is also cooperating with the Hong Kong MTR Group to connect Binhaiwan Bay Station with Hong Kong’s West Kowloon Station to build an integrated station with multiple rail links. The transportation network will allow residents to travel from Binhaiwan to Shenzhen in just six minutes, to Guangzhou in 35 minutes, and to Hong Kong in 40 minutes.
It is expected that by 2025, the population of the area will increase from the current less than 100,000 to more than 250,000, achieving a GDP of RMB 50 billion (US$7.7 billion), and by 2035, it will achieve a GDP of RMB 200 billion (US$ 30.8 billion) and a population of 500,000.
Dongguan Waterfront Economic Development Zone
Dongguan Waterfront Economic Development Zone is the first provincial strategic economic zone with waterfront characteristics as a development theme in Guangdong province.The zone enjoys superior geographic location and convenient transportation. Thanks to its abundant river water system resources, sufficient eco-land resources, rich waterfront culture of Lingnan Region, excellent tourism resources and urban agricultural conditions, the zone is vigorously developing the industries related to health services, energy saving and environmental protection, and cultural innovation.
Guangdong Dongguan GDH Yinping Cooperative Innovation Zone
Guangdong Dongguan GDH Yinping Cooperative Innovation Zone is a provincial project co-developed by Dongguan government and Guangdong Holdings Limited. It was built to be a primary hub for auto parts industries. The zone covers various areas for the automobile spare parts manufacturing, new energy vehicle manufacturing, automobile commerce, and trade exhibition area.Dezan Shira & Associates has handled multiple foreign investments into southern China over the years. We have offices in China, Vietnam, Singapore, and elsewhere in ASEAN and can therefore assist at both ends of the manufacturing supply chain. For more information and for support in investing in Dongguan and China’s Greater Bay Area, you are welcome to email us at china@dezshira.com.