Xiamen is among China's fastest-growing cities by GDP growth. Its economy is diversifying and modernizing, building upon its mainstay shipping and manufacturing industries and developing high-tech and modern service capabilities. With a dynamic industrial and business landscape in place as well local preferential policies for incoming companies, this seaside city offers a wide range of growth prospects for foreign investors.
Xiamen is a sub-provincial city located in the south-eastern province of Fujian. Perched on the western shoreline of the Taiwan Strait, the city has historically enjoyed a position as an important seaport, in particular for the export of tea, porcelain, and paper. In modern times, the city’s trade has shifted to the import and export of commodities such as foodstuffs and crude oil, as well as cross-border e-commerce, in particular electronics. Xiamen was one of the first cities to reopen to foreign trade and investment during China’s reform and opening-up period. In 1981, it was designated as one of just four ‘special economic zones’ (SEZ), areas that are granted looser restrictions on international trade and investment, as well as preferential policies aimed at accelerating development.  Today, the city’s economy is diversifying and modernizing fast. Powered in large part by booming international trade and a thriving shipping and logistics industry, the city has successfully protected itself from the worst of the pandemic. At the same time, emerging industries, such as fintech, high-end manufacturing, and high-end technology are finding fertile ground in which to grow, cultivated by beneficial government policies.
Today, the city’s economy is diversifying and modernizing fast. Powered in large part by booming international trade and a thriving shipping and logistics industry, the city has successfully protected itself from the worst of the pandemic. At the same time, emerging industries, such as fintech, high-end manufacturing, and high-end technology are finding fertile ground in which to grow, cultivated by beneficial government policies.
With its growth-friendly environment and strategic position on China's southeast coast, the city offers exciting prospects for foreign investors in a wide range of industries.Did you know? Xiamen was historically known to outsiders as ‘Amoy’. The name comes from the Hokkien dialect that is still widely spoken in Fujian province.
Xiamen’s economic profile
Over the past five years, Xiamen has maintained a higher level of economic growth compared to both the provincial and national averages, with an average annual growth rate of 7.4 percent from 2016 to 2020. Even as the COVID-19 pandemic took its toll, Xiamen’s 2020 GDP growth rate beat national averages, increasing 5.7 percent to RMB 638.4 billion (US$98.5 billion). That is 3.4 percentage points above the national average and 2.4 percentage points above the provincial average.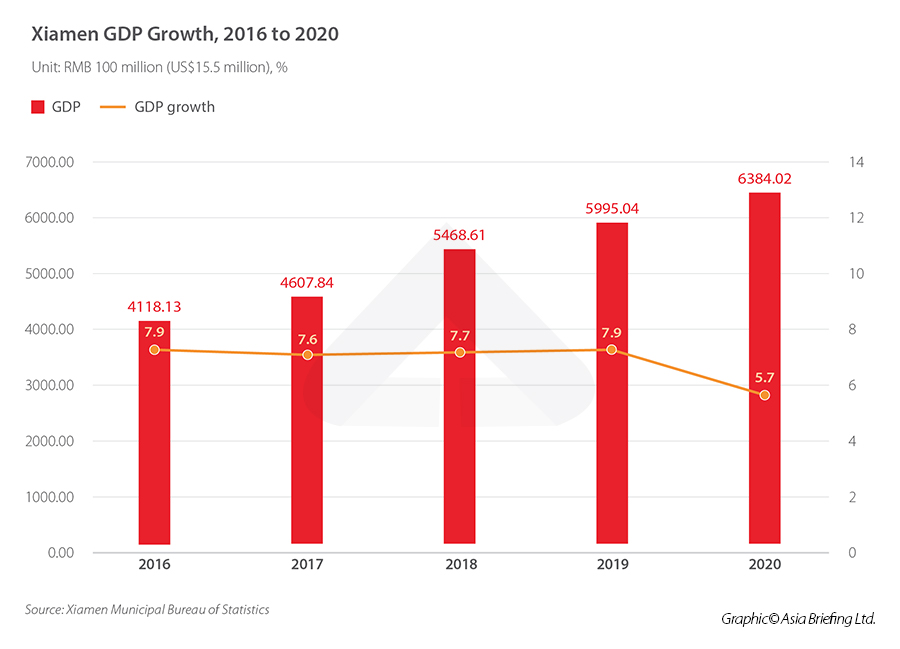 Meanwhile, Xiamen’s economic composition has also undergone a significant shift over the past decade. Tertiary sectors surpassed 60 percent of the local GDP for the first time in 2020, marking an inexorable turn toward reliance on the services for economic growth, a trend seen in many cities across the country.
Meanwhile, Xiamen’s economic composition has also undergone a significant shift over the past decade. Tertiary sectors surpassed 60 percent of the local GDP for the first time in 2020, marking an inexorable turn toward reliance on the services for economic growth, a trend seen in many cities across the country. 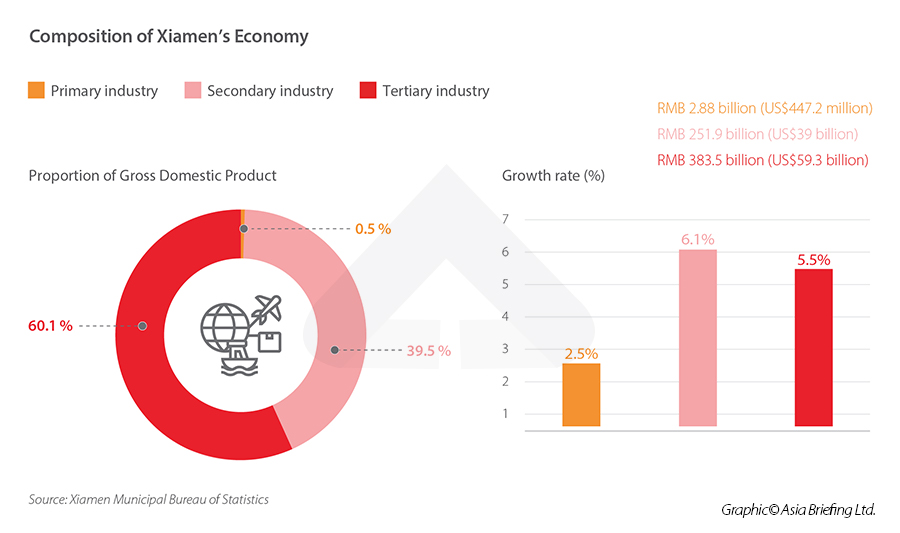 Xiamen was able to absorb the worst of the impact of the pandemic thanks in large part to strong trade and investment numbers in 2020, both of which saw positive growth from the previous year. The total volume of import-export reached RMB 691.58 billion (US$107 billion), an all-time high. Xiamen’s biggest foreign trade partners in 2020 were ASEAN, the U.S., and the European Union, which made up 43 percent of overall trade. Trade with countries that form part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) also grew 13.2 percent year-over-year to reach RMB 229 billion (US$35.5 billion). Actual use of foreign capital in 2020 was similarly positive, seeing a 23.8 percent year-over-year growth to reach RMB 16.6 billion (US$2.6 billion). This accounts for almost half of the total foreign direct investment (FDI) in the entire province. The majority (65.2 percent) of foreign capital went to the services sector, in particular industries like leasing and business services, accommodation and catering, and wholesale and retail. Foreign capital use in high-tech service industry R&D and design services increased 1.3-fold year-over-year.
Xiamen was able to absorb the worst of the impact of the pandemic thanks in large part to strong trade and investment numbers in 2020, both of which saw positive growth from the previous year. The total volume of import-export reached RMB 691.58 billion (US$107 billion), an all-time high. Xiamen’s biggest foreign trade partners in 2020 were ASEAN, the U.S., and the European Union, which made up 43 percent of overall trade. Trade with countries that form part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) also grew 13.2 percent year-over-year to reach RMB 229 billion (US$35.5 billion). Actual use of foreign capital in 2020 was similarly positive, seeing a 23.8 percent year-over-year growth to reach RMB 16.6 billion (US$2.6 billion). This accounts for almost half of the total foreign direct investment (FDI) in the entire province. The majority (65.2 percent) of foreign capital went to the services sector, in particular industries like leasing and business services, accommodation and catering, and wholesale and retail. Foreign capital use in high-tech service industry R&D and design services increased 1.3-fold year-over-year. 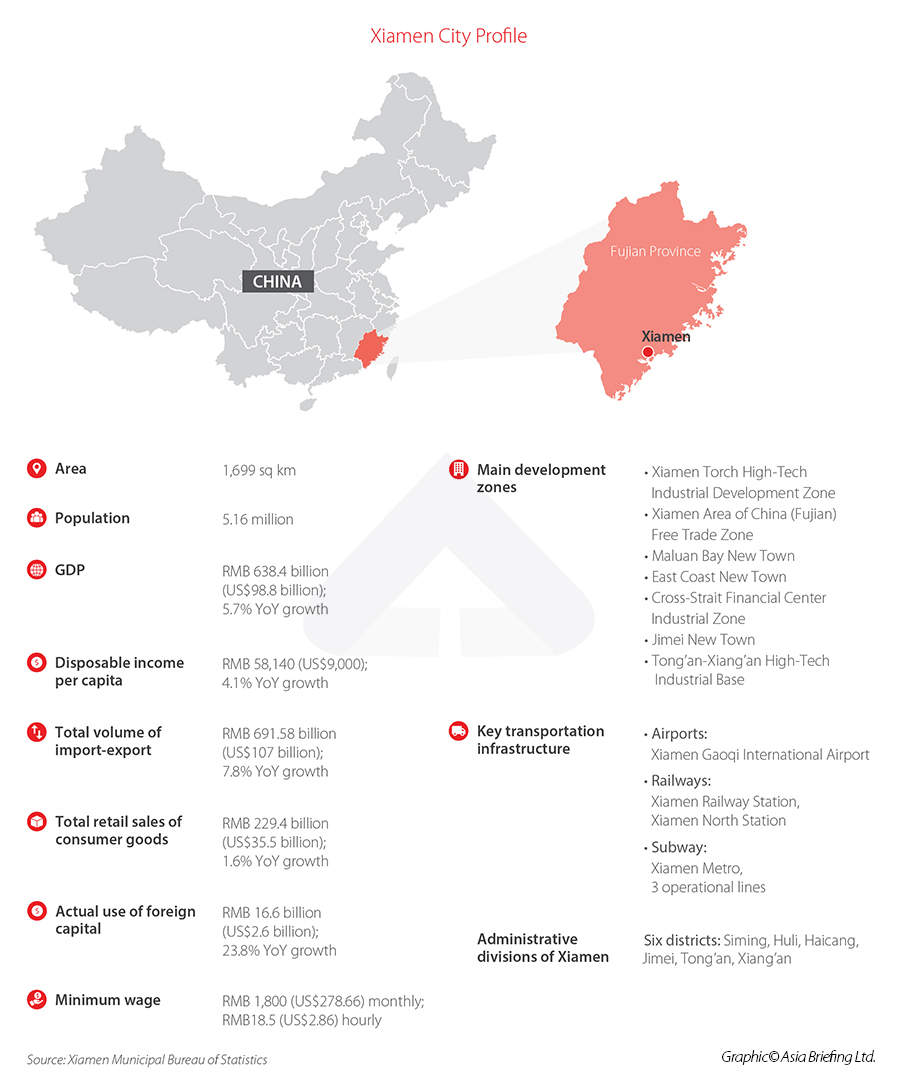
Labor market
Xiamen has a relatively young and well-educated workforce when compared to other cities in the region. According to the 2020 population census, the average age of the city’s population is 36.8 years, six months younger than the provincial average and two years younger than the national average. However, the city is currently on the brink of becoming an ‘ageing society’, with the proportion of over-60s at 9.56 percent, just shy of the 10 percent threshold for official designation. The population is also increasingly well-educated and Xiamen is home to some of China’s most renowned universities, most notably Xiamen University. Among the over-15 population, the average number of years of education has risen from 10.29 in 2010 to 11.17 in 2020. In the meantime, the number of people with a university education per 100,000 grew from 17,799 to 26,940.Xiamen’s mainstay industries
Electronics and machinery manufacturing
Xiamen’s economy still heavily relies on its two largest mainstay industries: electronics and manufacturing. In 2020, the total output value of these two industries reached RMB 496.7 billion (US$76.9 billion), accounting for almost 70 percent of the city’s total industrial output value of enterprises above a designated scale. (Note that “enterprises above a designated scale” is a technical designation used by Chinese statisticians to denote industrial companies with an annual income of RMB 20 million or more deriving from its main business (US$3.1 million).) Some of the most significant sub-fields within the electronics industry are flat panel displays, computers and communication equipment, liquid crystal display (LCD) components, and integrated circuits (ICs). In 2020, the total industrial output value for the flat panel displays and communication equipment industry broke RMB 100 billion (US$15.5 billion). The industrial output value of machinery and equipment manufacturing enterprises above a designated size reached RMB 225.2 billion (US$34.8 billion), an average annual growth rate of 9.9 percent. Among major sub-fields within this industry are automotive, electrical appliances, aircraft maintenance, general equipment manufacturing, and special equipment manufacturing. Major companies operating in this space in Xiamen include Toshiba, Fujitsu, Boeing, LG, and Japan Airlines, to name a few.Hi-tech and advanced manufacturing industries
As with many cities across China, Xiamen is seeking to future-proof its economy by increasing focus and investment on high-tech and ‘strategic emerging industries’. These are industries that are considered key to China’s overall technological development, such as high-end equipment manufacturing, biopharmaceuticals, new energy, and new energy vehicles. Much of the high-tech industry is concentrated in the Xiamen Torch High-Tech Industrial Development Zone, which seeks to cultivate emerging industries, including ICs, microelectronics, high-end equipment manufacturing, and biopharmaceuticals, and has attracted multinationals such as Panasonic, AU Optronics, and Nippon Electric Glass. The industrial output value of high-tech companies above a designated size reached RMB 76.6 billion (US$11.8 billion) in 2020, accounting for 39.8 percent of the city’s overall industrial output value.Modern services
Having surpassed the 60 percent of overall GDP mark, Xiamen’s service industry is accumulating many of the trappings of a maturing economy. ‘Traditional services’, such as postal and courier services, retail and wholesale, remain an important section of the economy, while new modern services, such as software and information services, modern logistics, and fintech, are gaining significant ground. Xiamen has a well-developed financial industry, which realized RMB 78.4 billion (US$12.1 billion) in added value in 2020, a year-over-year increase of 5.3 percent. The city is striving to become an influential financial hub and develop innovative financial sectors, in particular fintech. To encourage development in this area, a Financial Technology Industrial Park is currently being built in Siming District. Companies that set up within the park will be eligible for a variety of monetary rewards and support, including rent subsidies, rewards for economic contribution, and tax benefits for high-level talent. Due in part to its pleasant weather and environment, Xiamen has hosted many high-profile conferences and forums and has a thriving conference and exhibition industry and ample infrastructure to host large corporate and political events.Maritime industries
Xiamen’s economy is still relatively dependent on maritime industries: in 2020, gross ocean product (GOP) reached RMB 140.529 billion (US$21.7 billion), accounting for 22 percent of the local GDP. Much of this economic activity is conducted through the Port of Xiamen, an important deep-water port and a key shipping and logistics hub for the wider region. Located in the northwest of Xiamen Island, the port is the eighth largest in China and consists of nine container terminals. Industries that support the trade and shipping sector are therefore many in number and have been an important driver of the city’s post-pandemic recovery. Transportation, warehousing, and postal industries accumulated a total operating income of RMB 34.2 billion (US$5.3 billion) in the first half of 2021, a year-over-year increase of 29.7 percent. The municipal government is also seeking to promote recreational maritime sectors, such as recreational fishing, cruises, yachting, and sailing, and other ocean-related leisure industries.City-wide incentive policies
The main city-wide policies on foreign investment currently in place in Xiamen were laid out in a document released in 2018, titled Several Measures for Promoting Foreign Investment in Xiamen. The measures seek to encourage investment in the city’s priority industries for development, namely, flat panel displays, computers and communication equipment, ICs, machinery and equipment, tourism and exhibitions, modern logistics, software and information services, financial services, and the culture and creative industries.Incentives for investment in key industries
Foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) that invest in Xiamen’s priority industries with an annual foreign capital amount of at least US$10 million between the years 2018 and 2022 are eligible for the following rewards:- A one-off reward of 2 percent of the annual actual paid-in foreign capital, capped at RMB 20 million (US$3.1 million) per company.
- When the annual actual paid-in foreign capital reaches US$10 million, 100 percent of the corporate income tax (CIT) and the portion of the value-added tax (VAT) retained locally will be rewarded in the first two years, and 50 percent in the next three years, starting from the year the company began paying VAT.
- Set up in Xiamen between the years 2018 and 2022.
- Set up in Xiamen prior to January 1, 2018 but invest at least US$10 million in annual actual paid-in foreign capital between 2018 to 2020.
- Set up a project in Xiamen through a merger or acquisition between 2018 and 2020.
Incentives for setting up R&D centers
Foreign companies and institutions are encouraged to set up R&D centers in Xiamen and to cooperate with domestic companies on R&D. Certain eligible FIEs can enjoy nationwide benefits such as deductions and subsidies for R&D expenses, and applicable preferential policies for high-tech companies, innovation platforms, and technological R&D centers. Foreign R&D centers that purchase domestic equipment that meets certain requirements may also be eligible for full refunds of VAT. The document also pushes for simplifying import procedures for products such as samples and reagents.Incentives for talent
Employees of FIEs that invest in Xiamen’s priority industries between 2018 and 2020, with an annual actual paid-in foreign capital of at least US$10 million, may also be eligible for certain tax incentives, beginning from the year the company reaches US$10 million in annual actual paid-in foreign capital. Below are some incentives given to employees.- Employees that pay an annual individual income tax (IIT) of RMB 80,000 (US$12,369) or above are eligible for a refund of the portion of IIT that is retained locally. The proportion of the locally retained IIT that is subsidized is calculated based on the amount paid annually, broken down as follows:
- 50 percent subsidy for annual IIT payments of RMB 80,000 (US$12,369).
- 75 percent subsidy for annual IIT payments between RMB 80,000 (US$12,369) and RMB 250,000 (US$38,654).
- 100 percent subsidy for IIT payments in excess of RMB 250,000 (US$38,654).
- The subsidies are limited to a period of five years.
- Non-Xiamen residents (who are Chinese nationals) who pay more than RMB 50,000 (US$7,730) in IIT are eligible to purchase commercial housing as Xiamen residents.
- Non-Xiamen residents (who are Chinese nationals) who continue working at the company after three years and have paid social insurance for this duration are eligible to apply for local household registration, known as the hukou.












