EU-China Relations – Trade, Investment, and Recent Developments
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and French President Emmanuel Macron are making a joint visit to China this week. The visit comes amid fraught EU-China relations and is likely to revolve around a series of contentious issues. However, it also comes after two years of strong trade between China and the EU and follows a series of dialogues between Chinese and European leaders aimed at deepening economic ties. We look at EU-China trade and investment numbers over the last few years and discuss the sometimes tense bilateral relations.
The President of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen is visiting China from April 5 to 7, 2023, along with French President Emmanuel Macron. During their visit, the two leaders will hold a joint meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping.
Meanwhile, in a regular press conference on April 3, Chinese Foreign Spokesperson Mao Ning also stated that President Xi will hold talks with President Macron in order to “chart the course for bilateral relations, deepen China-France and China-EU cooperation in various fields, and have an in-depth exchange of views on major international and regional hotspot issues.” The French President is also expected to meet with other high-level Chinese officials and visit Guangzhou in Guangdong Province, reportedly to meet with a group of students.
The visit comes during a fraught time for EU-China relations, with relations cooling as a result of a range of issues and in particular geopolitical tensions. On March 31, von der Leyen gave a speech in which she advocated for a more hardline approach toward relations with China, drawing criticism from Chinese officials.
At the same time, strong bilateral trade figures serve to counter the pessimistic narrative, suggesting that mutual interest and reliance remain strong, and prompting von der Leyen herself to state that economic decoupling is not an option.
In the run-up to these high-stakes meetings, we look at the development of EU-China bilateral trade, investment, and diplomatic relations in recent years.
The development of EU-China relations
The EU and China formally established diplomatic relations in 1975, when the EU was made up of only nine member states. In the decades since, the relationship has developed to become one of strategic importance for the global economy, particularly as China emerged from the 20th century as a growing economic power and the world’s main manufacturing hub. The relationship has been largely built on bilateral trade, with the EU becoming increasingly reliant on Chinese manufactured goods, especially since China’s accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001. By 2020, bilateral trade between China and the bloc reached around EUR 1.8 billion per day.
Politically, bilateral relations have been relatively complex, defined at once by mutual reliance and opposing political stances. In recent years, relations have cooled significantly as European governments have taken a hardening stance toward various disputes, including alleged human rights issues, unequal market access, as well as the perceived growth of Chinese influence in Europe.
Relations have become even tenser in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, as China and the EU have found themselves on opposite sides of the conflict. Much of the rhetoric coming from EU leaders on China today is closely concerned with its relationship with Russia, with the EU urging China to use its influence over Russia to push for peace.
At the same time, EU countries have come under increasing pressure from the US, one of the EU’s closest allies, to side with it in its own campaign against Chinese activity, in particular as it pertains to the containment of Chinese technological development. For instance, EU governments and companies have come under pressure from the US to uphold its ban on chip exports to China, which has put companies like the Dutch chip company ASML in the crossfire.
It is also notable that, despite the tense relationship, EU-China trade has boomed over the last few years, indicating that the two regions maintain close economic ties and are highly reliant upon one another.
EU-China trade continues to record rapid growth
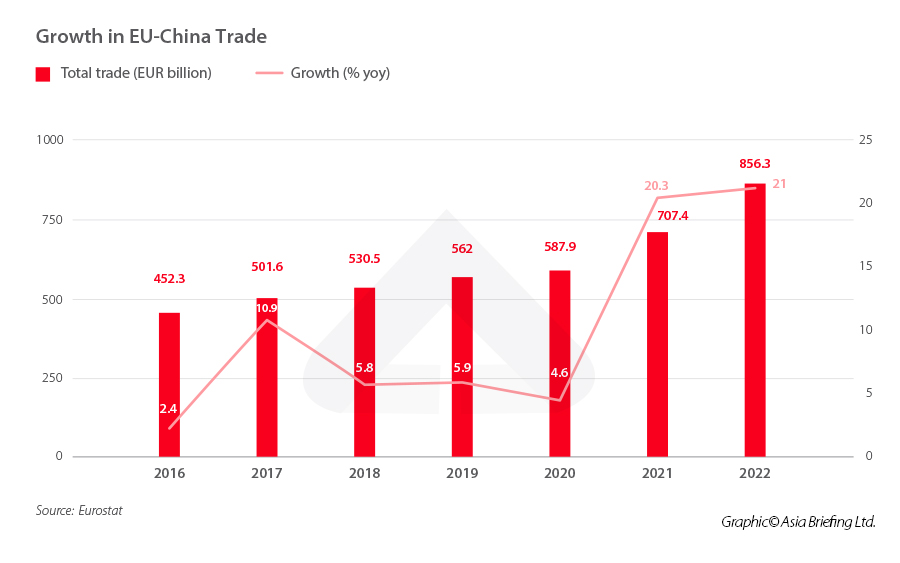
EU-China trade has grown rapidly in the last two years, accelerating from just 4.6 percent year-on-year growth in 2020 to over 20 percent year-on-year growth in 2021 and 2022. This acceleration has been driven mainly by China’s exports to the EU and is in line with China’s overall strong trade numbers over this period. The growth in China’s exports is in part thanks to the sharp increase in demand in western countries for Chinese-made goods during the pandemic.
China was the EU’s second-largest trade partner in 2022 behind the US, with total imports and exports reaching EUR 856.3 billion, according to data from Eurostat. This accounts for around 15.3 percent of the EU’s total trade that year.
The EU had a trade deficit of EUR 395.7 billion in 2022, expanding further from EUR 250.3 billion in 2021. Only one EU member state – Ireland – recorded a trade surplus with China in 2022. China remains the EU’s largest source of imports, with total imports reaching EUR 626 billion, accounting for 20.8 percent of all EU imports in 2022.
China is the third largest destination for EU exports, after the US and the UK, with exports to China reaching EUR 230 billion in 2022, accounting for 9 percent of the EU’s total exports.
China’s largest trade partner within the EU in 2022 was Germany, with total trade reaching EUR 236.9 billion, according to Eurostat data. Germany was also the largest exporter of goods to China, with total exports reaching EUR 106.9 billion. However, the Netherlands was the largest importer of Chinese goods, with total imports reaching EUR 130 billion.
The top-traded goods between the EU and China are machinery and vehicles, other manufactured goods, and chemicals. China’s top export goods to the EU in 2022 were telecommunications equipment, followed by automatic data processing machines, and electrical machinery and equipment. Meanwhile, the EU’s top exported goods to China are motor cars and vehicles, electronic tubes and valves, and auto components.
While machinery and vehicles dominate two-way trade, there are many other important trade industries. For instance, Europe remains highly reliant on China for light manufactured goods, such as toys, furniture, textiles, apparel, and footwear, while several EU countries also export significant amounts of food and agricultural products to China, as well as niche specialty products, such as leather goods and alcohol.
| EU-China Trade by Country, 2022 | |||||
| Country | Imports from China (EUR Million) | Exports to China (EUR Million) | Total imp-exp (EUR Million) | Main import goods from China | Main export goods to China |
| Germany | 130,030 | 106,853 | 236,883 | Electrical machinery and equipment; mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Organic chemicals; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Vehicles; precision instruments and medical devices; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories (including knitted or crocheted); toys; plastics | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Wadding, felt and nonwovens; special yarns; twine; Copper and articles thereof; electrical machinery and equipment; Articles of iron or steel; precision instruments and medical devices; Plastics; Tanning or dyeing extracts; |
| Netherlands | 138,790 | 18,691 | 157,481 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Toys; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; organic chemicals; plastics; precision instruments and medical devices; articles of iron or steel; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories (including knitted or crocheted); Vehicles; Mineral fuels, mineral oils | Electrical machinery and equipment; Plastics; Rubber; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Organic chemicals; precision instruments and medical devices; Beverages, spirits and vinegar; Residues and waste from the food industries; Paper and paperboard; Vehicles; Clocks and watches and parts thereof; Miscellaneous articles of base metal; footwear |
| Italy | 57,506 | 16,442 | 73,948 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Organic chemicals; Iron and steel; Plastics; Vehicles; precision instruments and medical devices; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Articles of iron or steel; footwear | Preparations of vegetables, fruit, nuts or other parts of plants, Nickel and articles thereof, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, precision instruments and medical devices, Beverages, spirits and vinegar, pharmaceutical products |
| France | 49,035 | 23,705 | 72,740 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Furniture; bedding, mattresses, toys, Articles of apparel and clothing accessories (including knitted or crocheted), vehicles, precision instruments and medical devices, plastics | Wood and articles of wood; Mineral fuels, mineral oils; Electrical machinery and equipment; precision instruments and medical devices; Copper and articles thereof; Miscellaneous chemical products; Edible fruit and nuts; peel of citrus fruit or melons; Organic chemicals; Beverages, spirits and vinegar |
| Spain | 41,981 | 8,013 | 49,994 | Electrical machinery and equipment; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; vehicles; furniture; bedding, mattresses; articles of apparel and clothing accessories (including knitted or crocheted); toys; plastics; articles of leather; animal or vegetable fats and oils and their cleavage products; precision instruments and medical devices; miscellaneous chemical products | Electrical machinery and equipment, Mineral fuels, mineral oils, Wood and articles of wood, Fish and crustaceans, mollusks, Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, precision instruments and medical devices |
| Belgium | 35,251 | 7,774 | 43,025 | Vehicles, electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, organic chemicals, plastics, furniture, toys, iron and steel, footwear | Wood and articles of wood, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, salt; sulphur; earths and stone; plastering materials, lime and cement, vehicles, residues of waste food, Aluminum and articles thereof, Electrical machinery and equipment |
| Poland | 37,597 | 2,958 | 40,555 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Plastics; articles of iron or steel; Vehicles; toys; inorganic chemicals; precision instruments and medical devices; Organic chemicals; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories (knitted or crocheted); miscellaneous chemical products | Copper and articles thereof; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Electrical machinery and equipment; precision instruments and medical devices; miscellaneous chemical products; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Organic chemicals; pharmaceutical products; Mineral fuels, mineral oils |
| Czech Republic | 30,058 | 2,592 | 32,650 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Vehicles, plastics, Articles of iron or steel, toys, Furniture; bedding, mattresses, precision instruments and medical devices, Articles of apparel and clothing accessories | Ores, slag, and ash, residues and waste from the food industries, prepared animal fodder, copper and articles thereof, electrical machinery and equipment, cereals, precision instruments and medical devices |
| Ireland | 12,260 | 13,033 | 25,293 | Organic chemicals; mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Electrical machinery and equipment; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Toys; articles of apparel and clothing accessories (knitted or crocheted); Articles of iron or steel; Plastics; precision instruments and medical devices | Pulp of wood or of other fibrous cellulosic material, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Electrical machinery and equipment, precision instruments and medical devices, ores, slag, and ash, Wood and articles of wood, Dairy produce; birds’ eggs; natural honey |
| Sweden | 13,404 | 6,741 | 20,145 | Electrical machinery and equipment; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; furniture; bedding, mattresses; articles of apparel and clothing accessories (including knitted or crocheted); articles of iron or steel; vehicles; toys; plastics; precision instruments and medical devices; footwear; other made-up textile articles; inorganic chemicals; articles of leather; ships, boats and floating structures | Vehicles; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; electrical machinery and equipment; Wood and articles of wood; Plastics; precision instruments and medical devices; footwear; miscellaneous articles of base metal; aluminum and articles thereof; rubber; copper and articles thereof; furniture; bedding, mattresses |
| Denmark | 12,294 | 5,672 | 17,966 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Furniture; bedding, mattresses, Articles of apparel and clothing accessories (including knitted or crocheted), Articles of iron or steel, Ships, boats and floating structures, toys, plastics | Copper and articles thereof; Electrical machinery and equipment; Pulp of wood or of other fibrous cellulosic material; salt; sulphur; earths and stone; impregnated, coated, covered or laminated textile fabrics; Cork and articles of cork; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Fish and crustaceans, mollusks |
| Austria | 9,139 | 5,178 | 14,317 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical requirements, nuclear reactors, organic chemicals, furniture, precision instruments and medical devices, chemical products, toys, plastics | Machinery, mechanical appliances; wood and articles of wood; electrical machinery and equipment; mineral fuels, mineral oils and products of their distillation; precision instruments and medical devices; ores, slag and ash; articles of iron or steel; plastics; vehicles; copper and articles thereof; Rubber; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; pharmaceutical products |
| Hungary | 12,476 | 1,722 | 14,198 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors; precision instruments and medical devices; Miscellaneous chemical products; Vehicles; Plastics; Articles of iron or steel; | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; pulp of wood or of other fibrous cellulosic material; electrical machinery and equipment and parts thereof; wood and articles of wood; vehicles; precision instruments and medical devices; plastics; miscellaneous chemical products; articles of iron or steel; iron and steel; rubber and articles thereof; toys; aircraft, spacecraft, and parts thereof |
| Finland | 4,558 | 4,035 | 8,593 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; articles of iron or steel, Ships, boats and floating structure, Furniture; bedding, mattresses, Articles of apparel and clothing accessories, Mineral fuels, mineral oils | Salt; sulphur; earths and stone; mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Mineral fuels, mineral oils and products; Ores, slag and ash; Pharmaceutical products; Dairy produce; birds’ eggs; natural honey; tools, implements, cutlery, spoons and forks, of base metal; precision instruments and medical devices; |
| Romania | 7,381 | 1,085 | 8,466 | Electrical machinery and equipment; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; precision instruments and medical devices; furniture; bedding, mattresses; plastics; vehicles; articles of iron or steel; toys; organic chemicals; rubber; aluminum and articles thereof; footwear; irons and steel; miscellaneous chemical products | Vehicles, machinery, electrical machinery, mechanical requirements, nuclear reactors, precision instruments and medical devices, pharmaceuticals, man-made staple fibers, plastics |
| Slovenia | 7,883 | 444 | 8,327 | Organic chemicals; electrical machinery and equipment and parts thereof; vehicles; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Plastics; toys; articles of iron or steel; (articles of apparel and clothing accessories, knitted or crocheted); footwear; furniture; bedding, mattresses; precision instruments and medical devices; Iron and steel; articles of leather; miscellaneous chemical products | Meat and edible meat offal, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Fish and crustaceans, mollusks, precision instruments and medical devices, Electrical machinery and equipment, Miscellaneous chemical products, Albuminoidal substances; modified starches; glues; enzymes |
| Greece | 7,908 | 408 | 8,316 | Electrical machinery and equipment; mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; toys; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories (knitted or crocheted); Paper and paperboard; Footwear; plastics | Electrical machinery and equipment; mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; precision instruments and medical devices; Pharmaceutical products; Miscellaneous manufactured articles; Vehicles; iron and steel; Toys |
| Slovakia | 4,580 | 2,615 | 7,195 | Electrical machinery and equipment; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; vehicles; articles of iron or steel; precision instruments and medical devices; plastics; miscellaneous articles of base metal; toys; furniture; bedding, mattresses; other base metals; cermets; articles thereof; tools, implements, cutlery, spoons and forks, of base metal | Electrical machinery and equipment; Pharmaceutical products; Organic chemicals; precision instruments and medical devices; aircraft, spacecraft, and parts thereof; Natural or cultured pearls, precious or semi-precious stones, precious metals; Preparations of cereals, flour, starch or milk; pastrycooks’ products; mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers |
| Portugal | 5,543 | 629 | 6,172 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Vehicles; organic chemicals; Plastics; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Articles of iron or steel; Iron and steel; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories; precision instruments and medical devices; Articles of leather | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; vehicles; pharmaceutical products; electrical machinery and equipment; Iron and steel; plastics and articles thereof; paper and paperboard; pulp of wood or of other fibrous cellulosic material; precision instruments and medical devices; wood and articles of wood; organic chemicals; miscellaneous chemical products; ores, slag and ash |
| Bulgaria | 3,186 | 777 | 3,963 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, Furniture; bedding, mattresses, Vehicles, plastics, Organic chemicals, precision instruments and medical devices | Electrical machinery and equipment, Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, precision instruments and medical devices, Pulp of wood or of other fibrous cellulosic material, Wood and articles of wood, Toys, vehicles, plastics, articles of iron or steel |
| Lithuania | 1,995 | 100 | 2,095 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Vehicles; Plastics; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; precision instruments and medical devices; organic chemicals; articles of iron or steel; miscellaneous articles of base metal; toys | Pharmaceuticals, machinery, plastics, precision instruments and medical devices, organic chemicals, wood and wood articles, electrical machinery and equipment, other vegetable textile fibers |
| Croatia | 1,391 | 86 | 1,477 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, furniture; bedding, mattresses, precision instruments and medical devices, tobacco and manufactured tobacco substitutes, toys, plastics | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Copper and articles thereof; Electrical machinery and equipment; precision instruments and medical devices; Wood and articles of wood; vehicles; Dairy produce; birds’ eggs; natural honey; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Plastics; Pharmaceutical products; Rubber; Articles of iron or steel; Inorganic chemicals |
| Estonia | 1,189 | 210 | 1,399 | Electrical machinery and equipment, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Articles of iron or steel, Furniture; bedding, mattresses, plastics, toys, precision instruments and medical devices, Vehicles, organic chemicals | Meat and edible meat offal; ores, slag and ash; pharmaceutical products; plastics; machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; vehicles; copper and articles thereof; electrical machinery and equipment; animal or vegetable fats and oils and their cleavage products; essential oils and resinoids; perfumery, cosmetic or toilet preparations; beverages, spirits and vinegar |
| Latvia | 995 | 230 | 1,225 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Miscellaneous chemical products; Rubber; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Plastics; precision instruments and medical devices; Articles of iron or steel; Tobacco and manufactured tobacco substitutes | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; pharmaceutical products; vehicles; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories; articles of leather; Electrical machinery and equipment; precision instruments and medical devices; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Footwear |
| Republic of Cyprus | 896 | 25 | 921 | Ships, boats and floating structures, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Electrical machinery and equipment, Organic chemicals, Furniture; bedding, mattresses, Articles of iron or steel, plastics, rubber | Aircraft, spacecraft, and parts thereof, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers, Articles of leather; Essential oils and resinoids, pharmaceutical products, Beverages, spirits and vinegar, Electrical machinery and equipment, cereals, Articles of apparel and clothing accessories |
| Luxembourg | 311 | 249 | 560 | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Electrical machinery and equipment; Plastics; Miscellaneous chemical products; articles of iron or steel; Man-made filaments; Ceramic products; precision instruments and medical devices; Tanning or dyeing extracts | Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Pharmaceutical products; Preparations of cereals, flour, starch or milk; precision instruments and medical devices; Electrical machinery and equipment; plastics; Meat and edible meat offal; Wood and articles of wood; vehicles; organic chemicals; Dairy produce; birds’ eggs; natural honey |
| Malta | 370 | 59 | 429 | Electrical machinery and equipment; Machinery, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Organic chemicals; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories; plastics; Articles of apparel and clothing accessories; Furniture; bedding, mattresses; Articles of leather; Articles of iron or steel; Toys; Footwear; Vehicles; precision instruments and medical devices | Vehicles, mechanical appliances, nuclear reactors, boilers; Electrical machinery and equipment; precision instruments and medical devices; Pharmaceutical products; Aircraft, spacecraft, and parts thereof; plastics; inorganic chemicals; Miscellaneous chemical products |
| Source: Eurostat, ICT Trade Map | |||||
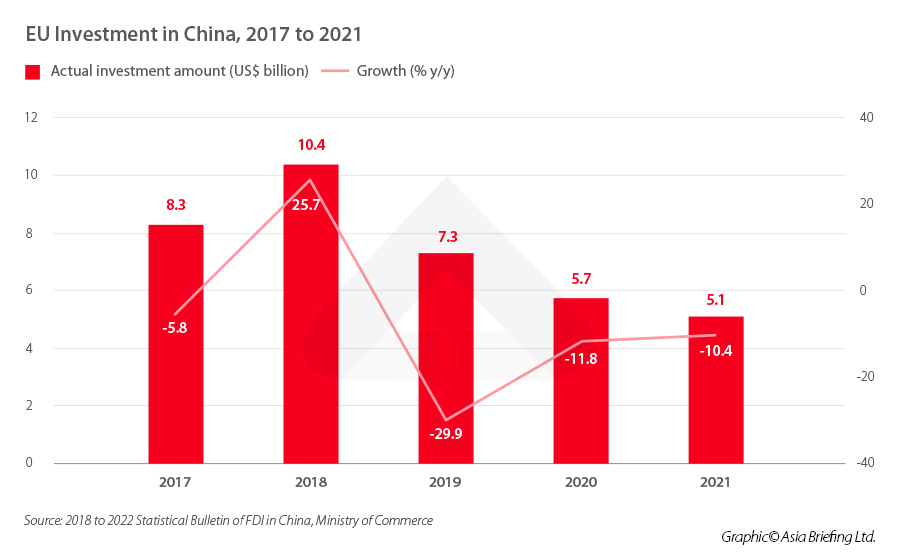
EU investment in China decreases but may be on the rebound
Investment from EU countries into China saw sharp drops in the years between 2019 to 2021. According to data from China’s Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM), actual use of foreign capital from EU countries dropped from US$7.3 billion in 2019 to US$5.7 billion in 2020, a year-on-year decrease of 11.8 percent. This dropped further to US$5.1 billion in 2021, a year-on-year decrease of 10.4 percent.
The fact that the decline in EU investment in China began even before the pandemic suggests that the issue may be more systemic, with EU companies blaming the difficulties faced by EU countries in entering the China market.
However, preliminary growth data from 2022 suggests that the numbers may have bounced back. Data from MOFCOM shows that EU countries’ investment in China increased by 92.2 percent year-on-year in 2022.
It is tempting to look at this jump and say that EU investment in China is recovering, but it is possible this sudden reversal is the result of a few very large projects that took place in 2022, such as large investments from German companies Volkswagen and BASF, rather than a sign of an improving trend.
China-EU trade and investment treaties
China currently has active bilateral investment treaties (BITs) with all EU countries except Ireland. These BITs guarantee protection to investors and their investments from both contracting countries in the other contracting country, as codified by the most-favored-nation (MFN) clause. They also usually include clauses on dispute mechanisms in the event, including arbitration in a neutral international court.
In addition, China has signed avoidance of double taxation agreements (DTAs) with France, Belgium, Germany, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, the Netherlands, Poland, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Spain, Romania, Austria, Hungary, Malta, Luxembourg, Croatia, Slovenia, Lithuania, Latvia, Portugal, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia.
There are currently no trade or investment treaties between China and the EU as a bloc. In late 2020, the EU and China reached an agreement in principle on an investment deal called the Comprehensive Agreement on Investment (CAI). The CAI is a landmark agreement, in which China committed to improving market access and ensuring equal treatment for EU companies. This includes commitments to implementing “terms of disciplines for state-owned enterprises, transparency of subsidies and rules against the forced transfer of technologies.”
However, following China’s sanctions on several EU MEPs, the approval process for the agreement was halted, and negotiations have not resumed since.
Recent EU-China dialogue
Despite the ongoing tensions, China and the EU have maintained open lines of communication, and recent months have seen several high-profile visits and dialogue between EU and Chinese officials. In early November 2022, the new German Chancellor Olaf Scholz visited China, the first G7 leader to do so since the start of the pandemic. The meetings revolved around furthering bilateral economic cooperation, including promoting fair trade between the two countries.
The same month, President Xi also met with French President Macron at the sidelines of the G20 Summit in Bali, in which the French President reportedly stated that France is ready to “deepen cooperation in areas such as trade, economy, aviation, and civilian nuclear energy” and that “France welcomes Chinese firms to the country for business cooperation”.
In February 2023, China’s top diplomat and former Foreign Minister Wang Yi took a tour of Europe in which he visited France, Italy, Hungary, and Russia, and attended the Munich Security Conference. During the tour, Wang met with several high-level European officials, including President Macron and the President’s Diplomatic Advisor Emmanuel Bonne, the Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister of Italy Antonio Tajani, and the Hungarian Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade Peter Szijjarto. These meetings largely revolved around reestablishing and developing trade and business relations in the post-COVID era and also touched upon China and the EU’s role in peacemaking in the Russia-Ukraine war.
On March 31, the Prime Minister of Spain Pedro Sánchez met with President Xi Jinping during a state visit to China, as well as several business leaders. In addition to discussing issues surrounding the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the Prime Minister also announced two phytosanitary protocols for China to buy more Spanish persimmons and almonds, “for which the Chinese market has enormous potential”.
EU-China relations expected to persist amid tensions
EU and China still have very different stances on a series of issues, but EU-China relations and engagement are expected to persist in the foreseeable future.
For example, in President von der Leyen’s speech ahead of her visit to China, she criticized China’s “no-limits” relationship with Russia and stated that “how China continues to interact with Putin’s war will be a determining factor for EU-China relations going forward”, indicating that the EU’s stance toward China has not softened. However, she also emphasized that the EU would not seek to decouple its economy from China, calling instead for “de-risking”. She also called for continued dialogue and cooperation with China, stating that “our relationship with China is far too important to be put at risk by failing to clearly set the terms of a healthy engagement”.
It is also important to note that there are 27 countries in the EU, and there is therefore a diversity of opinions when it comes to cooperation with China. For instance, China’s relationship with Hungary has been considerably more amicable than that of other EU countries in recent years, and the country also broke ranks with the rest of the EU to welcome China’s Ukraine peace plan.
In addition, President Macron’s visit to China will almost certainly not solely be to discuss the current issues pertaining to the Russia-Ukraine war, but also be a concerted effort to further develop China-France trade and business ties. In fact, the French president is bringing a group of business leaders with him on the trip, including officials from French multinationals Airbus and Alstrom. These moves strongly suggest that Macron’s goals for his trip to China are starkly different from those of President von der Leyen and that France will ultimately not seek to distance itself further from China.
Dezan Shira & Associates’ Presence in Europe
Europe has significant trade and investment dealings with Asia – China, ASEAN, and India are all among the bloc’s top trade partners. With Asia emerging as a growth engine of the world economy and an area of certainty amid global volatility, there is a wealth of opportunities for European investors in the region. Incorporated in Munich in January of 2021, Dezan Shira & Associates’ European office under Riccardo Benussi serves as a first point of contact for European companies wishing to do business in Asia. Meanwhile, our Europe-based team in both the Munich and Milan offices works with a variety of partners to connect European businesses with developing Asian economies. To set up a call with our Europe-based team, please contact riccardo.benussi@dezshira.com.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article Top Recruitment Strategies in China in the Post-COVID Era
- Next Article Investing in China’s Greater Bay Area: Tapping into Long-Term Opportunities – New Dezan Shira & Associates Publication