China’s FTZ Count Rise to 21 After Beijing, Hunan and Anhui Are Newly Added
- China has announced new free trade zones in Beijing, Hunan, and Anhui and expands the Zhejiang FTZ.
- Each zone has adopted policies to promote regional industrial clusters building upon the unique strengths and characteristics of the area.
- Beijing and Zhejiang pilot FTZs will lead technical and digital innovation, while Anhui and Hunan will emphasize the high-quality development of their advanced manufacturing sectors.
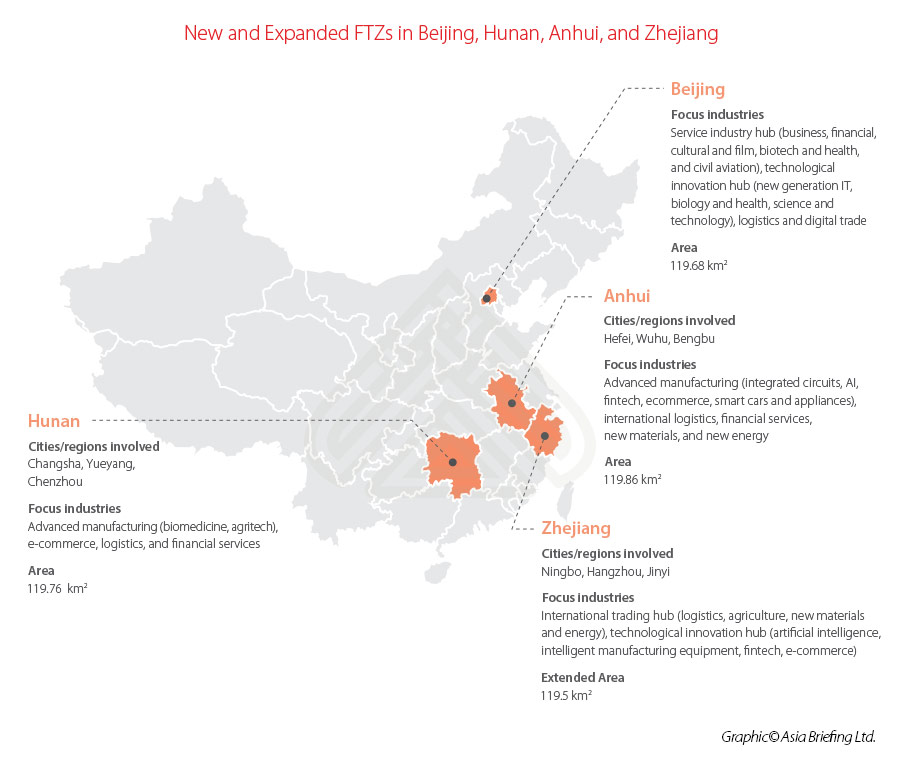
On September 21, China’s State Council announced that it will establish three new pilot free trade zones (FTZs) in Beijing, Hunan, and Anhui and expand the FTZ in Zhejiang.
Pilot free trade zones are areas marked out by the government where a series of test policies are trialed, such as tax cuts, streamlined customs clearance, and/or industry-specific liberalization, which will be replicated and scaled up to the national-level if they are successful.
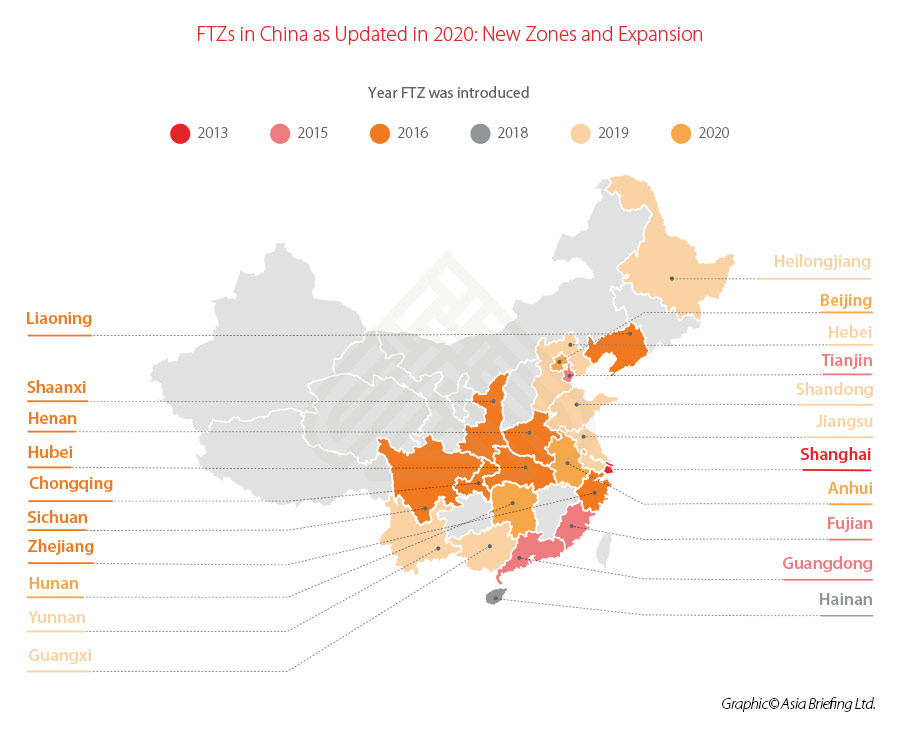
This is the seventh batch of FTZs announced since 2013, taking China’s total tally to 21 free trade zones spread across the country.
What distinguishes each zone from the next is their respective regional industrial agglomeration. This generates tremendous opportunities for foreign investors as companies can take advantage of being close to respective networks of suppliers, service providers, and specialist labor pools.
We examine the latest FTZ plan, strategic priorities of each zone, the types of preferential policies that businesses can expect, and the potential implications for businesses within these zones.
The latest pilot FTZ plan at a glance
The General Plan for the Construction of Three Pilot Free Trade Zones in Beijing, Hunan and Anhui and the Regional Expansion of the Zhejiang Pilot Free Trade Zone (“the Plan”) sets into motion the construction of three pilot free trade zones within China and expansion of the Zhejiang FTZ.
Across the board, there are some clear themes shared by all four FTZ locations:
- Opening-up of the financial sector;
- Investment reform
- Trade facilitation and innovation; and
- Promoting integrated development within its respective city-cluster or international trade channels.
These themes will be catered to differently from zone to zone as policies will play to the unique strengths and characteristics of the area.
For example, Beijing and Zhejiang FTZs are both positioned to lead technical and digital innovation in China; however, Beijing will focus more heavily on financial services opening-up and service trade innovation, whereas Zhejiang will prioritize smart logistics and e-commerce development for the purpose of creating an international trading hub.
Meanwhile, Anhui and Hunan will spotlight the high-quality development of their advanced manufacturing sectors – Anhui will focus on high-end technologies, such as integrated circuits, artificial intelligence (AI), fintech, and smart cars and appliances, whereas Hunan will concentrate on biomedicine, agritech, and e-commerce).
Beijing pilot FTZ
The zone will cover a total area of 119.68 square kilometers, comprised of three smaller areas:
- 85 square kilometers for science and technology innovation;
- 34 square kilometers for international business services; and
- 49 square kilometers for the development of high-end industries.
Central to the plan is the construction of a global innovation center, a leading area for the expansion of trade in services, and a pilot area for the digital economy. The Beijing FTZ will play a critical role in coordinating the development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
There are four tasks unique to the Beijing pilot FTZ:
New service trade management models
A negative list management model for cross-border trade in services will be implemented on a trial basis to gradually relax the market accessibility of service trade, where conditions permit. Within the early development stages of the respective supervision model, innovation will be actively encouraged in tracing and supervising enterprises, transaction documents, personnel, funds, and commodities in the zone.
The FTZ will also make it easier for ‘high-end talents’ to obtain a visa for the purposes of research and development, training, or exhibition participation.
Deepen the opening-up and innovation of the financial sector
The FTZ will strengthen the financial sector from three perspectives – expanding market accessibility, promoting innovation (such as fintech), and strengthening cross-border financial services of the real economy.
Within the FTZ, various pilot projects will be implemented for the expansion and opening-up of the finance sector. Some of these include:
- Establishment of a fintech center by the Digital Currency Research Institute of People’s Bank of China (PBC);
- Pilot zone for the legal development of digital currency and a digital financial system;
- Pilot zone for scenarios of fintech application;
- Formation of a standard system for trade finance blockchain based on the PBC’s trade finance blockchain platform; and
- Auto-financing companies in the region will be supported in carrying out cross-border financing.
High-quality development of advantageous industries
Four areas are identified by the plan as advantageous to China’s future development and priority areas for development – construction of international exchange centers, meeting cultural and film consumer demand, innovations in the medical and health industry, and the development of aviation services. The plan proposes various pilot projects to support the growth of these sectors, by way of small reforms in the administrative processes or facilitation of cross-border activity
Integrated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
The pilot free trade zone will encourage new ways of facilitating cross-regional cooperation in industrial supply chains and financing the technology market in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
Specifically, the following strategies were proposed to encourage a more coordinated system of development:
- Explore the pilot implementation of a more centralized administrative licensing system;
- Support the establishment a national voluntary emissions reduction;
- Simplify the process of introducing special talents; and
- Standardize the system of cross-border green credit asset securitization, green bond, and green equity investments.
Hunan pilot FTZ
The zone will cover a total area of 119.76 square kilometers, comprised of three smaller areas:
- 98 square kilometers in Changsha (high-end equipment manufacturing, new generation IT, biomedicine, e-commerce, and agricultural tech);
- 94 square kilometers in Yueyang (shipping logistics, e-commerce, and new-generation IT); and
- 84 square kilometers in Chenzhou (strategic hub, which will focus on connecting with the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, non-ferrous metal processing, and modern logistics).
The Hunan FTZ will construct a series of advanced manufacturing clusters in areas of high-end equipment, new generation IT, and non-ferrous metal processing. Complementing this, it will also focus on establishing an international investment and trade corridor linking the Guangdong-Hong Kong Macao Greater Bay Area and Yangtze River Economic Belt and will become a pioneer zone for deeper China-Africa economic and trade cooperation.
Five tasks unique to the Hunan pilot FTZ are:
Promote the high-quality development of trade
Main measures include improving the transport and links between the bonded zones and airport, improving the international rail freight combined transport, and upgrading current trade processes, such as the ore-blending business.
The FTZ will also focus on cultivating new forms of trade, such as cross-border e-commerce, entry-exit of cultural relics, as well as film and television products.
Support the high-quality development of advanced manufacturing
The zone will act to promote the digital and intelligent transformation of the manufacturing industry, support the construction of an industrial Internet platform, and increase the construction of public service platforms.
This zone will focus on the development of new-generation information technology, biomedicine, e-commerce, and agricultural technology, among others, and will construct a global high-end equipment manufacturing base and high-end modern services industry center.
Deepen opening and innovation of the financial sector
Within the zone, a pilot program will be carried out for qualified overseas limited partners (QFLP) of foreign-invested equity investment enterprises. Furthermore, the zone will relax the application conditions for foreign investors to establish investment companies – the requirement for total assets of foreign investors in the year before the application is reduced to no less than US$200 million (RMB 1.36 billion) and the requirement for the number of foreign-invested enterprises established in China by foreign investors is eliminated.
Create new links to surrounding regions in China
Deeper coordination along the Yangtze River Economic Belt will be achieved by cooperating on matters of customs clearance, trade statistics, inspection, certification, supervision, and enforcement.
Joint development of the service industry between Hunan and the Guangdong-Hong Kong- Macao Greater Bay Area will be achieved by practicing a mutual recognition of qualifications and actively promoting industries, such as creating 5G videos and setting up an e-sports base.
To facilitate closer trade ties between the Greater Bay Area and the Central China, an intelligent logistics hub will be built in Hunan, Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao.
Explore new paths and mechanisms for China-Africa economic trade and cooperation
The plan also indicates that a pilot zone for in-depth economic and trade cooperation between China and Africa will be constructed in order to experiment with different ways to ignite local cooperation between the two countries.
Anhui pilot FTZ
The zone will cover a total area of 119.86 square kilometers, comprised of three smaller areas:
- 95 square kilometers in Hefei (integrated circuits, artificial intelligence, fintech, and cross-border ecommerce);
- 35 square kilometers in Wuhu (smart connected cars, smart home appliances, aviation, robotics, and shipping); and
- 91 square kilometers in Bengbu (silicon-based materials, bio-based new material, and new energy).
The Anhui FTZ will focus on the construction of an advanced manufacturing center for integrated circuits, artificial intelligence, fintech, quantum computing, new energy, and new materials. It will also focus on e-commerce and support the integrated development of the Yangtze River Delta and Belt and Road.
Five tasks unique to the Anhui pilot FTZ are:
Promote high quality development trade
This zone will support the construction of the Hefei and Wuhu comprehensive cross-border e-commerce pilot zones and support these areas to carry out cross-border e-commerce retail import trials. Parallel to this, the FTZ will carry out cross-border e-commerce RMB settlement in accordance with laws and regulations and promote the innovation of cross-border e-commerce online financing and guarantee methods.
Deepen innovation and opening-up of the financial sector
Most notably, the plan proposes relaxing the proportion of foreign ownership of financial institutions, broadening the business scope of foreign financial institutions, and supporting qualified domestic and foreign investors to establish various financial institutions in accordance with the law. In addition, within the zone, a study and implementation of a pilot policy will be carried out for qualified foreign limited partners/QFLP.
Innovation-driven development
A six-in-one mechanism will be established for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements of government, industry, university, research, and research funds. The zone will also help to conjure up support for the construction of relevant national technological innovation centers (particularly in the areas of energy, artificial intelligence, advanced computer science, and health material science).
Promote industry optimization and upgrading
The zone will generate a new batch of national strategic emerging industrial clusters, including but not limited to – biomedicine, high-end smart equipment, new energy vehicles, and silicon-based new materials.
The plan will support the National Advanced Manufacturing Industry Investment Fund in investing in new energy vehicles, new displays, robots, and other industries and will actively identify high-tech enterprises that meet the requirements in the key areas of integrated circuit, artificial intelligence, biomedicine, and civil aviation.
Within the zone, an advanced layout of future industries will be designed featuring quantum computing and quantum communications, biological manufacturing, and advanced nuclear energy.
Integrated development in the Yangtze River Delta, Yangtze River Economic Belt, and Belt & Road construction
Most notably, the zone will promote the coordinated development of pilot free trade zones in the Yangtze River Delta and support the joint development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. It will also participate in the co-building of scientific and technological innovation communities with countries and regions along the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and support the construction of the infrastructure along this route.
Zhejiang pilot FTZ
The extended zone will cover a total area of 119.5 square kilometers, comprised of three smaller areas:
- 46 square kilometers in Ningbo (international shipping hub that links internal and external multimodal transportation as well as building an oil and gas resource allocation center);
- 51 square kilometers in Hangzhou (new-generation artificial intelligence, fintech, e-commerce, and digital economy); and
- 99 square kilometers in Jinyi (commodity capital, digital trade, logistics, and manufacturing)
The plan focuses on the construction of a new type of international trading center, an international shipping and logistics hub, and the construction of a commodity resource allocation base centered on oil and gas.
There are four tasks unique to the Zhejiang pilot FTZ expanded area, these are:
Construct a global resource allocation base for bulk commodities centered on oil and gas
Centered around the idea of energy and food security, the Zhejiang pilot FTZ will build a global resource allocation base for the storage of bulk commodities.
Oil and gas will be a central component of these plans – with the FTZ pledging to introduce a series reforms on matters relating to supply chain optimization, reserve management, and space utilization.
The Zhejiang pilot FTZ plan will also actively expand agricultural trade cooperation with other countries and vigorously develop high-end animal protein processing and trade industries, such as imported beef.
The FTZ proposes the construction of a storage and transit base for imported grains and will implement innovative quarantine examination and approval system for grain import.
At the same time, it will allow non-tariff quota grain to be examined and approved by port storage and determine processing sites after import (except for active genetically modified agricultural products).
Build an international shipping and logistics hub
To construct a world-class international shipping and smart logistics hub within the zone, new intelligent internet services will be experimented with within the four ports – seaports, dry ports, airports, and information ports – and an international transshipment transfer business warehouse will be explored.
The feasibility of implementing the port of departure tax rebate policy will be tested in Ningbo Zhoushan Port. At the same time, the FTZ will reinforce the management model of bonded marine fuel oil supply and allow liquefied natural gas (LNG) to enjoy the bonded policy as fuel for international sailing ships. Finally, the FTZ will also build a cross-port fuel supply system for the Yangtze River Delta port group, and work together to build a fuel oil refueling center in Northeast Asia.
Digital economy development
The zone will create a demonstration zone for the development digital economy supported by new generation digital infrastructure. It will also strengthen the research and formulation of international rules and standards in the field of digital economy and promote mutual trust and recognition in the standards industry.
Financial institutions within the zone will be encouraged to innovate their financial services and products, while venture capital companies will be guided to invest in innovative and entrepreneurial projects in the digital economy.
Top domestic and foreign companies will also see investment promotion efforts intensified in areas, such as cloud manufacturing, artificial intelligence, big data, and industrial Internet research and development
Create an advanced manufacturing cluster
The Zhejiang Pilot FTZ expansion plan proposes the creation of an advanced manufacturing cluster, supported by an “dual-circuit supply policy system”, whereby key components are sourced both internationally and domestically. Within the plan, there will be a strong focus on the application of core technology within the supply chain of new materials industry and the life and health industries.
The FTZ will also put forth import taxation policies to support scientific and technological innovation and exempt tax for imported scientific research equipment that aligns with policy requirements.
The zone will also speed up independent research and development, pilot-scale conversion, and equipment finalization in emerging fields, such as seawater desalination and comprehensive utilization, and marine renewable energy, and actively promote the large-scale development of the industry.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
We also maintain offices assisting foreign investors in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, United States, and Italy, in addition to our practices in India and Russia and our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative.
- Previous Article What is China’s Dual Circulation Strategy and Why Should Foreign Investors Take Note?
- Next Article Chinas FTZ-Zahl steigt auf 21, nachdem Peking, Hunan und Anhui neu hinzugekommen sind