China’s Vocational Education Reform and Foreign Investment Opportunities
Although China is tightening regulations on academic tutoring for school-age students, it is simultaneously encouraging private investment in vocational education. China believes upskilling its workforce is key to the country’s continued economic growth. Foreign investment is explicitly welcome in the vocational education sector.
On October 12, 2021, the Communist Party Central Committee and the State Council issued the Guidelines on Promoting the High-Quality Development of Modern Vocational Education (hereafter “Guidelines”). The document sets clear goals, including that by 2025, the enrollment of vocational colleges should be no less than 10 percent of the total enrollment of higher education institutions; and by 2035, China’s vocational education should be among the best in the world.
Moreover, contrary to its recent abrupt crackdown on for-profit tutoring in core education, China has been constantly pushing for the accelerated development of its vocational education system for many years.
The objectives behind these actions are not contradictory.
Policymakers want to reduce the workload of students and ensure educational equity, besides increasing the supply of skilled workers to meet the demands of an economy transitioning to advanced industry and technology-led growth. This could signal long-term changes to China’s education landscape.
Thus, while foreign stakeholders are banned from investing in China’s compulsory education segments (Grade 1-9, six years at primary schools and three years at junior secondary schools) or religious education, vocational education (including vocational school education and vocational training) is an area that explicitly welcomes foreign investment.
Generally, foreign investment in pre-school education, ordinary high school, higher education institutions, and vocational education institutions must be conducted in cooperation with and under the leadership of a Chinese entity. This must be read differently from the investment environment in China’s vocational education industry. Recent moves by the Chinese government include policies to relax market access to the vocational education segments for foreign investors.
The significance of vocational education for China’s future
China has been pushing for the expansion of its vocational education system for many years.
Latest efforts include revising the Vocational Education Law, announcing a three-year action plan, and granting subsidies to enterprises that set up apprenticeship programs.
These policy actions aim to upskill the Chinese workforce and the benefits are clear. If Chinese rural and low-income workers are well-educated and trained to meet the needs of high-end manufacturing sectors (like chip manufacturing, new energy, modern agriculture, industrial robots, etc.), they will propel and sustain the economy’s ambitious growth targets. Otherwise, under-skilled workers could slow down growth capacity and create critical skill gaps in the talent market.
Currently, China is facing a structural imbalance in its job market with an oversupply of university graduates but a shortage of highly skilled factory workers. The imbalance has been intensified since the COVID-19 pandemic, with more factory workers seeking more flexible service jobs (like food delivery and courier services), resulting in fewer factory workers.
Developing vocational education can help China address its unemployment pressures and the labor market imbalance. It can also indirectly boost the “rural rejuvenation” and “common prosperity” campaigns and ultimately avoid the country falling into the middle-income trap.
What’s standing in the way of China’s vocational education development
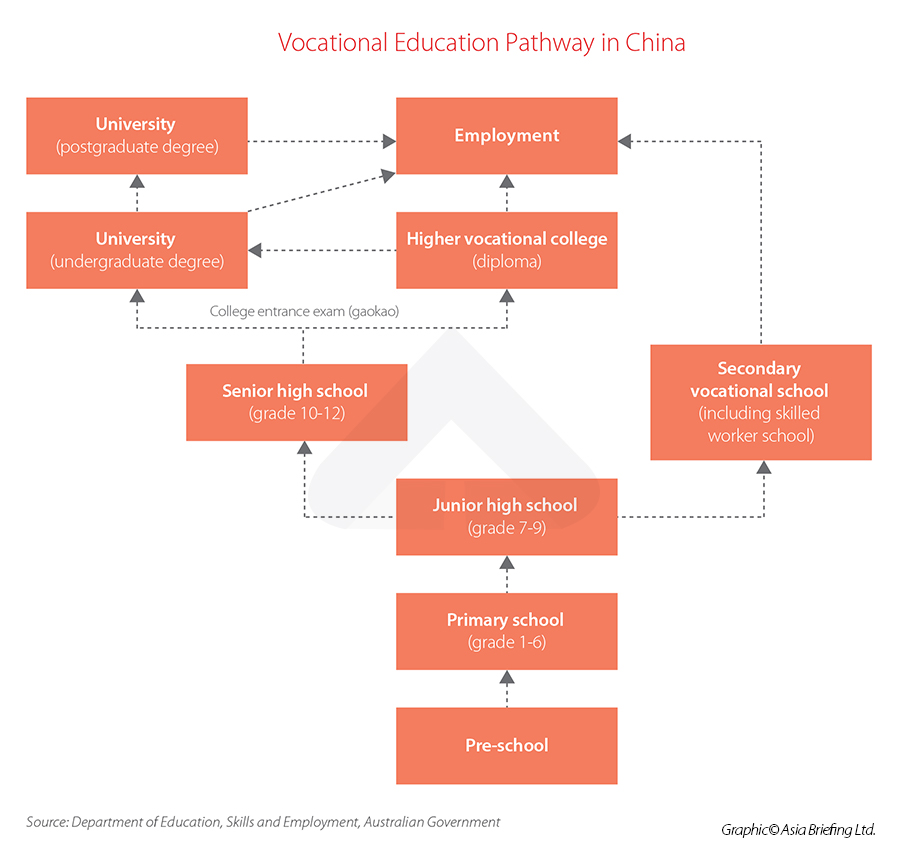
At present, Chinese kids can go to a secondary vocational school after finishing their nine-year compulsory education (Grade 1-9) or go to a higher vocational college after finishing senior high school (Grade 10-12).
Often overlooked, secondary vocational school students make up roughly 40 percent of the high school-age population in China – more than 16 million kids at last count, according to Sixth Tone. However, the quality of secondary vocational education in China is low and the schools have disproportionately high dropout rates. Many kids end up taking jobs that are irrelevant to their majors. Most, having graduated or dropped out of schools, went into ordinary factories or service sectors.
As for higher-level vocational education, in 2020, China had nearly 1,500 registered higher education institutions (including universities and higher vocational colleges) but out of them, only 21 were vocational colleges, according to Caixin.
In the 2020 Government Work Report, China introduced its plan to provide more than 35 million vocational skill training opportunities and increase enrollment in vocational colleges by two million over the next two years. And it intends to subsidize 75 million vocational training slots in the next few years through 2025.
However, in addition to the poor quality of vocational education and the small number of higher vocational colleges, another worry is that vocational education is widely considered by Chinese people as a “second choice” to an academic degree. Most parents are not willing for their children to study in a vocational school unless there is no option.
Now policymakers are trying to raise the status and the social recognition of vocational education. The latest draft version to the Vocational Education Law states that “vocational education is as important as regular education”.
China’s measures to improve vocational education
In the Guidelines as well as other relevant policy documents, we’ve noted the following reform measures adopted or to be adopted by the government:
- Introduce the “vocational college entrance exam” (China already has the famous National College Entrance Exam, or “Gaokao”, for high-school students to gain admission to universities and colleges.) The “vocational college entrance exam”, however, is expected to be open to vocational school graduates, workers, and the unemployed. And it will assess a mix of cultural knowledge and professional skills.
- Encourage listed companies and industry-leading enterprises to run vocational education programs and to participate in developing curriculum and teaching materials of vocational institutions.
- Encourage vocational schools to set up majors that meet market demand. Priority should be given to training talent for emerging industries, including advanced manufacturing, renewable energy, modern agriculture, and artificial intelligence (AI).
- Encourage vocational institutions to step up cooperation with enterprises to serve technological upgrading and product research in medium, small, and micro businesses.
- Encourage undergraduate schools to develop “vocational undergraduate education”.
- Primary and middle school students should receive formative courses on vocational education to cultivate their awareness of career planning.
- Improve the quality of teachers, innovate teaching models, and promote overseas cooperation.
- Cooperate with other countries and international organizations to share new perspectives in vocational education and training.
Are foreign investors allowed to invest in China’s vocational education?
The vocational education sector is steadily opening to foreign investors. The 2020 negative lists for foreign investment permit wholly-foreign owned enterprises to establish vocational training institutions in China’s free trade zones (FTZs) without a domestic partner.
In addition, the State Council recently announced it will adjust the Regulation on Chinese-foreign Cooperative Education for Beijing to boost the capital’s services sector. Beijing will formulate specific management measures to encourage foreign investment in for-profit adult education and training institutions and for-profit vocational training institutions.
In fact, foreign investors are encouraged to invest in non-academic vocational training institutions nationwide, according to the Catalogue of Industries for Encouraging Foreign Investment. A total of 12 provinces – Shanxi, Liaoning, Anhui, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangxi, Hainan, Chongqing, Shannxi, Gansu, and Ningxia – explicitly welcome foreign capital in vocational schools (including technical schools) in their respective local investment catalogues.
China’s vocational education sector shows promising opportunities for foreign investors. The investment banking firm Morgan Stanley predicts that government support and market demand will see the vocational education market grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of seven percent in the decade from 2020 to 2030, as reported by CNBC.
China Briefing’s parent company, Dezan Shira & Associates, has helped foreign investors successfully enter the education market in Asia – from studying the market, managing investments, and structuring the business model at the pre-investment phase to managing statutory compliances and maintaining best practices once operational. For more information and assistance on the market entry, please feel free to contact us at China@dezshira.com.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China Makes Cryptocurrency Transactions Illegal: An Explainer
- Next Article PIPL China: Suggestions for Technical Compliance with Personal Information Protection Law