Hainan’s Negative List Creates Business Opportunities for Foreign Investors
On December 31, 2020, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) released the Special Administrative Measures for the Access of Foreign Investment in Hainan Free Trade Port (2020 Edition), also dubbed as the “Hainan FTP FI Negative List”, to be implemented from February 1, 2021. (You may find the full list in Chinese here.)
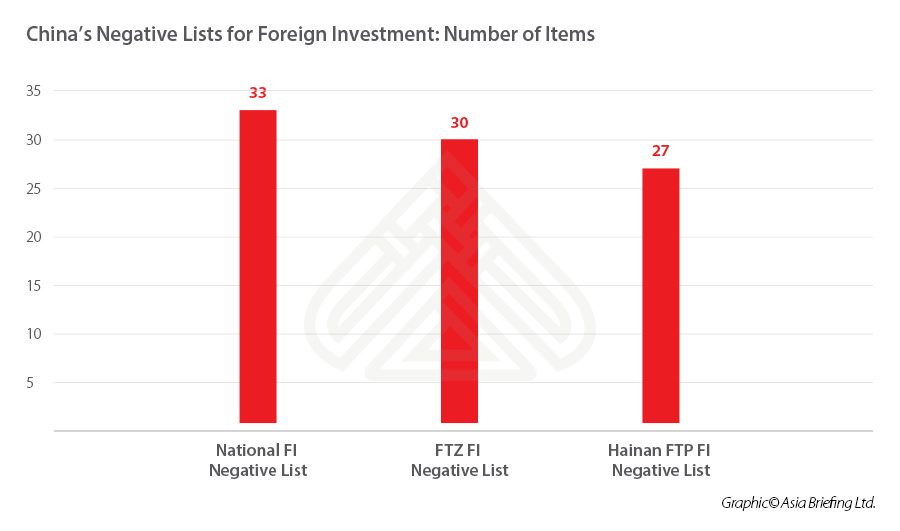
The Hainan FTP FI Negative List enumerates industries and sectors that restricts or prohibits foreign investment in Hainan island. The list includes a total of 27 items, fewer than the number of items in the national FI negative list and the FI negative list for free trade zones (FTZs), which indicates a higher degree of market openness in Hainan.
Expanded market access in Hainan
Ahead of other parts of the Chinese mainland, Hainan will expand market access to foreign investment in various sectors, such as telecommunications, education, business services, manufacturing, and mining.
Telecommunications
In value-added telecommunication services, Hainan will scrap restrictions on foreign investment in online data processing and transaction processing businesses. Enterprises with registered entities and service facilities in the Hainan FTP will be allowed to develop Internet data center and content distribution networks (CDN) to serve the Hainan FTP and international markets.
Education
Education sector-wide, overseas high-level universities specializing in science and engineering, agriculture, and medicine and vocational colleges will be able to run schools in Hainan independently.
Business services
In the fields of legal services, foreign investors will be allowed to engage in some non-litigation affairs involved in commercial matters in Hainan, to better meet the demand for foreign legal services in trade, investment, finance, and other fields in Hainan FTP.
Hainan also lifted bans on foreign investment in market surveys, except that broadcasting and television ratings survey should still be controlled by the Chinese party. Foreign investors can also conduct social investigations in the form of equity joint ventures. The Chinese party shareholding percentage should be more than 67 percent and the legal representative should be a Chinese citizen.
Manufacturing and mining
Hainan will take the lead in removing foreign investment limits in automobile manufacturing. The restriction on the foreign shareholding in the manufacturing of passenger cars and the requirement that one foreign investor may establish two or less joint ventures in China to manufacture the same type of vehicles will be removed in Hainan this February. This policy relaxation will be implemented nationwide in 2022.
In addition, Hainan will no longer prohibit foreign investment in the exploration, mining, and beneficiation of rare-earth, radioactive minerals, and tungsten.
Foreign investment in Hainan FTP
Since June 1, 2020 when China rolled out the masterplan to build Hainan island into a free trade port, Hainan has issued at least 78 policy documents to promote its development as a FTP, covering tax cuts in corporate income tax (CIT) and individual income tax (IIT), exemption on customs duties and import taxes, special customs supervision mechanisms, off-shore duty-free policy, and measures to facilitate the free flow of foreign talents and capital, to strengthen intellectual property protection (IPR), and to optimize business environment.
On December 31, 2020, the National People’s Congress released the Law of Hainan Free Trade Port (Draft), to gather public opinions until January 29, 2021. With 58 chapters, the draft law covers facilitation in free trade and investment, fiscal and tax systems, ecological and environmental protection, industrial development, and talent support, and is expected to provide a legal guarantee for the implementation of the Hainan FTP FI Negative List.
On January 13, 2021, the local provincial department of commerce released data about foreign investment in Hainan. The actual use of foreign investment in Hainan totaled about US$3 billion in 2020, doubling the figure of US$1.5 billion in 2019.
Services sector see most new entry – a total of 909 newly established foreign-funded enterprises, or 90 percent of all new foreign-funded enterprises are in the services sector. Modern business services, wholesales, and software and information technology services ranked the top three in the actual utilized foreign capital, with a year-on-year increases of 4.7 times, 10.5 times, and 6.2 times, respectively.
Eighty countries and regions are invested here, doubling the figure from 2019. Investors cover all G20 members, all RCEP partners except Brunei, 15 EU countries, including France, Germany, and Italy, and nearly half of the 65 countries along the “Belt and Road Initiative” route.
At a press conference in December 2020, the NDRC has pledged that it will continue to reduce the Hainan FTP FI negative list in the future.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
We also maintain offices assisting foreign investors in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, United States, and Italy, in addition to our practices in India and Russia and our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative.
- Previous Article Hong Kong, cosa c’è dopo? I punti di forza e i vantaggi su cui Hong Kong è stata costruita sono sufficienti per sostenere il suo futuro sviluppo economico?
- Next Article La politica energetica nell’accordo UE-Cina