Chongqing’s Growing Focus on the Electronics Industry and Digital Economy
- Liangjiang New Area in Chongqing is becoming a major hub for southwestern China’s digital economy and is seeking to drive development by deepening collaboration with member countries of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
- In 2019, the Liangjiang New Area established the Trade and Economic Multifunctional Platform for SCO member countries, a platform for cooperation in education and industry between Chongqing and SCO markets.
- In the week of August 23, 2021, Liangjiang New Area aimed to further boost collaboration by hosting two major forums, which have already produced significant results.
On August 23, 2021, the fourth China-Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Forum on the Digital Economy Industry kicked off in Liangjiang New Area in southwest China’s Chongqing Municipality, the same week as the city hosted the Smart China Expo 2021.
The forum was attended by representatives from all SCO countries – a regional organization comprised of eight mainly central Asian countries, as well as Russia and India – and the expo was participated in by more than 610 companies from 31 countries and regions.
The location of this year’s forum was strategically chosen, with the aim of “promoting common prosperity by developing the digital economy” by accelerating economic and trade cooperation between SCO countries and the Chongqing Liangjiang New Area. Digital economy is a loosely defined section of the economy, which incorporates a range of technology-driven sectors from electronics equipment manufacturing to software services.
Day one of the Smart China Expo witnessed the signing of 92 projects worth a total of RMB 250 billion (US$38.62 billion), demonstrating the vitality and potential of the digital economy. Both events were concluded on August 25, 2021.
Chongqing and the Trade and Economic Multifunctional Platform for SCO member countries
The China-SCO Forum on Digital Economy Industry is one of the five sub-forums of the Trade and Economic Multifunctional Platform for the SCO Countries (TEMP), a platform for cooperation in education and industry between Chongqing and the SCO markets.
- In February 2018, the then SCO Secretary-General Rashid Alimov led 12 diplomatic envoys from SCO member states to China to visit Chongqing and put forward a preliminary plan for Chongqing to build a multi-functional economic and trade platform for SCO member states.
- On August 24, 2019, the TEMP, jointly built by the SCO Business Council and Chongqing Liangjiang New Area, was officially established in the Liangjiang New Area of Chongqing.
Why Chongqing
Situated in inland China, the sprawling city of Chongqing is a key port along the Yangtze River economic belt and a prominent logistics node for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
According to SCO Secretary-General Vladimir Norov: “Chongqing is a unique link that connects entrepreneurs in the Asia-Pacific region, China’s inland provinces and Eurasian countries. It serves as a bridge in cooperation in electronics, transportation logistics, information technology and tourism for the SCO and ASEAN countries”
In 2020, trade between Chongqing and SCO markets (member states, observer states, and dialogue partners) reached RMB 50.9 billion (US$7.86 billion), up 15 percent year-on-year, among which the trade volume between Chongqing and SCO member states reached RMB 32.5 billion (US$5.01 billion).
Appeal of Chongqing Liangjiang New Area
Chongqing Liangjiang New Area is the first national-level development zone in inland China, and the third nationally after Shanghai Pudong New Area and Tianjian Binhai New Area.
It covers 1,200 square kilometers, and focuses on chips, liquid crystal panel, intelligent termina, and core parts. Major industries based here are the electronics information industry, general aviation, rail-transportation equipment manufacturing, emerging finance, international logistics, big data and information services, cross-border settlement, e-commerce, bonded trade and entrepot trade, and professional services, such as healthcare and tourism.
In recent years, the New Area has established an opening-up system extending in all directions and a modern industrial system. A total of 160 Fortune 500 enterprises have settled in Liangjiang, with several more international organizations, associations, and multinational enterprises joining the investment and settlement campaign in the New Area.
On April 9, 2021, the promotion meeting of Chongqing Liangjiang New Area-Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Countries Trade and Economic Multifunctional Platform was held in Beijing.
Chongqing’s growing focus on the electronics industry and digital economy
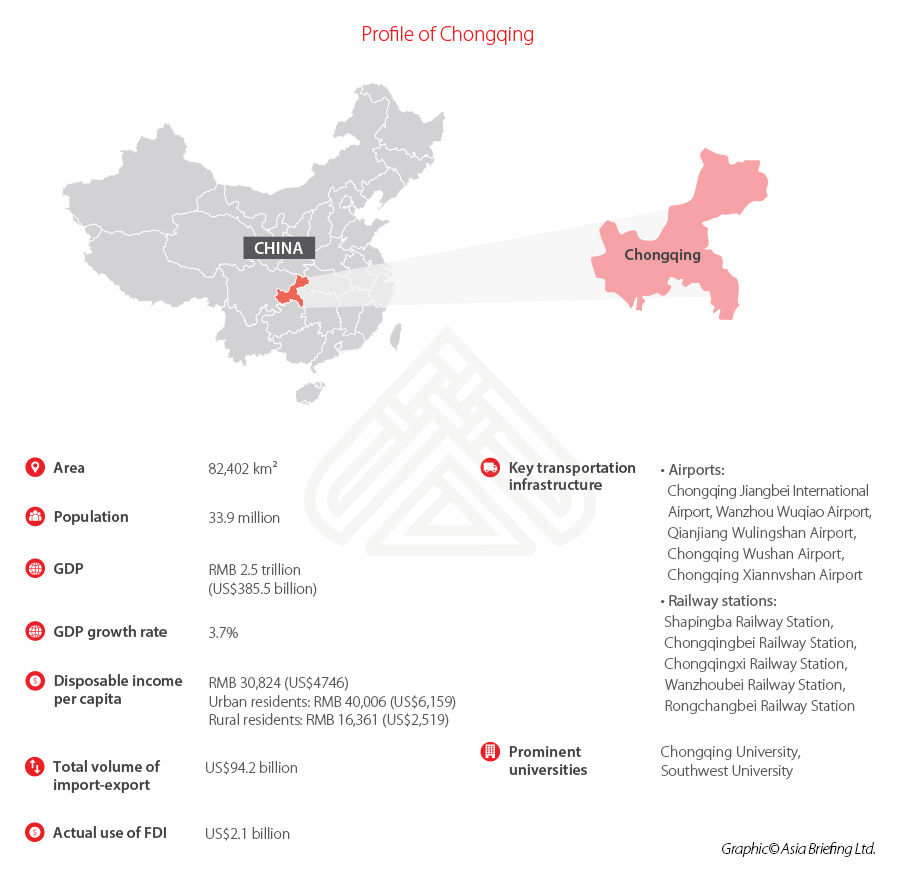
As China’s largest municipality by size and population, Chongqing ranks as the fifth Chinese city with the strongest GDP, following Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou. The city recorded a GDP of RMB 2.5 trillion (US$385.5 billion) in 2020. For perspective, that’s about the size of Israel’s or Argentina’s economy.
With relatively cheaper labor, well-developed infrastructure, integrated industrial clusters and supply chains, and sound business environment, as well as benefiting from national policies, Chongqing stands out as a major destination for foreign investment in China’s central and western regions.
Chongqing used to be one of China’s main old industrial bases, dominated by heavy industries, such as automobile manufacturing, military, iron, steel, and aluminum industries. In 2019, heavy industry still accounted for 79.5 percent of Chongqing’s gross industrial output. The city is the largest automobile and motorcycle manufacturing base in China.
Recent years has seen growing efforts to transform its industry, which has helped the rise of the city’s electronics industry and digital economy.
Striving to become a hub for advanced manufacturing, Chongqing is doubling down on developing its electronics industry, which has maintained strong momentum, growing 13.9 percent last year. The share of total gross industrial output of telecommunication equipment, computers, and other electronic equipment industries grew from 11.4 percent in 2012 to 23.8 percent in 2019. Today, Chongqing produces one-third of the world’s laptops and 90 percent of the world’s IT network terminals, making it the world’s largest laptop production base and the second largest mobile phone production base in the world.
In terms of sectors, Liangjiang New Area has created an electronics industry base dominated by three industrial clusters: integrated circuits (IC), display panels, and intelligent terminals. The New Area is now also striving to developits high-end equipment manufacturing industry, focused on areas such as computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools, 3D printing, laser manufacturing equipment, environmental protection equipment, rail transit equipment, and so on. The city is currently home to manufacturing giants Foxconn Technology, Isuzu, and ABB.
In the first half of 2020, the added value of the booming digital industries in Chongqing reached RMB 33.6 billion (US$5.19), a 55 percent growth year-on-year. Overall, Chongqing’s digital economy accounts for a quarter of the local economy, which boasts 6,000 companies in Liangjiang New Area.
In June 2020, Chongqing released plans to further shore up its digital economy. The plan indicates that Chongqing will foster hundreds of innovative companies and 5,000 micro, small, and medium firms in this sector by 2022.Chongqing also plans to invest RMB 398.3 billion (US$61.5 billion) into new infrastructure projects during 2020-2022 to promote the integration of the digital economy with the real economy.
According to Chongqing’s Municipal government, by 2022, Chongqing’s digital economy is expected to reach RMB 1 trillion (US$141.32 billion), accounting for over 40 percent of the city’s economy and contributing over 60 percent to the local GDP growth.
Investment opportunities in Chongqing’s digital economy
The Liangjang New Area, long an attractive investment destination, is following the playbook of many other major Chinese cities and seeking to transform its economy through a shift to high-tech manufacturing, digitization, and other emerging digital and technology industries.
In addition to its economic ambitions, Chongqing is seeking to strengthen its position as a key trade hub for the BRI, and by extension, expand influence with BRI countries, many of which are also SCO member countries. This is likely a large factor in Chongqing’s desire to promote the digital economy to SCO countries through measures such as the TEMP.
In June this year, China Education Group established an education service branch and ‘SCO Multifunctional Economic and Trade Platform Education Service Working Committee’, projects initiated through the TEMP. It also collaborated with Chinese supercomputing manufacturing company Sugon to promote a new educational infrastructure industrial park. Once completed, the park will provide super-computing services to universities in China and in SCO countries, thereby supporting education and scientific research in SCO countries.
Other efforts to promote collaboration with SCO countries
Other similar projects designed to build collaboration with SCO countries may be seen in the years to come.
In its broader push to promote the industry, Liangjiang issued a ‘1+3’ set of policy documents in 2020. These documents set out different policies and guiding opinions for developing the digital economy. One set of the guiding opinions proposed the construction of “three smart technology innovation platforms, five smart industry clusters, one smart manufacturing innovation corridor, and a demonstration of fully integrated smart city applications”.
The ‘demonstration of fully integrated smart city applications’ refers to the use of big data, cloud computing, blockchain, AI, and other technologies for smart city management, which will be implemented through the construction of a ‘City Brain’ and ‘Smart City Operation Center’.
Driving the future of Liangjiang’s digital economy
Under these plans, it is estimated that the revenue from Liangjiang’s digital economy will surpass RMB 500 billion by 2025.
The New Area is also home to several industrial parks dedicated to the development of the digital economy. One such place is the Chongqing Internet Industrial Park, which focuses on areas such as fintech, online education, cloud computing, big data, Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence, among other fields. The Chongqing Internet Industrial Park actively welcomes R&D institutes, software and information service providers, and high-tech companies to set up within its jurisdiction.
Meanwhile, the Digital Economy Industrial Park was established to develop important emerging industries, such as big data, ICs, software and information technology services, and digital integration industries.
There are great opportunities for investment and trade in this area. As said by Singapore’s Minister of Communication and Information: “The possibilities offered by digital revolution are cross-cutting and limited only by our imagination”.
International cooperation might be the only way to unlock the potential of digital technologies, as has been emphasized by the China-SCO Forum on Digital Economy Industries.
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article Belt and Road Weekly Investor Intelligence, #44
- Next Article China’s Taxpayer Credit Rating System: An Explainer