Shanghai Encourages Foreign R&D Centers, Introduces a Dozen Support Policies
On November 24, 2020, Shanghai’s Municipal Government released the Regulations on Encouraging the Establishment and Development of Foreign-funded Research and Development Centers (Hu Fu Ban Gui [2020] No.15) in a move to lure foreign investors, including those from Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan, to set up research and development (R&D) centers in Shanghai.
Consisting of 23 articles, the Regulations will be in effect from December 1, 2020 until November 30, 2025.
During this period, eligible foreign-funded R&D centers will benefit from a dozen policy support measures, including customs clearance facilitation for cross-border R&D, cross-border financial services facilitation, talent acquisition and development, funding support, tax cuts, participation in government projects, facilitation of environmental assessment and hazardous waste management, facilitation on land use for R&D purposes, and protection of intelligent property rights (IPRs), etc.
For more information or assistance on setting up a foreign-invested R&D center in Shanghai, please contact China@dezshira.com.
Shanghai’s status as an R&D hub
Shanghai has a big lead in attracting foreign R&D centers than any other Chinese city. According to official data, as of October 2020, 763 regional headquarters of multinational corporations (MNCs) have step up in Shanghai, as well as 477 foreign R&D centers, one-third of which were set up by Fortune Global 500 Companies. Most foreign R&D centers are concentrated in the biomedicine, information technology, auto parts, and chemical industries. This year, Shanghai welcomed 43 regional headquarters of MNCs and 16 foreign R&D centers.
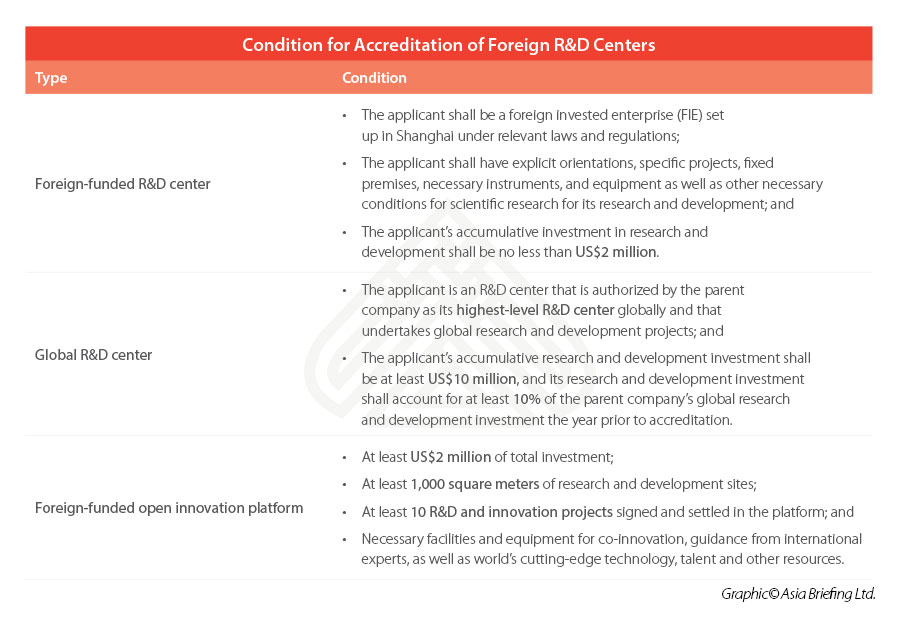
Definition and accreditation condition for foreign-funded R&D centers in Shanghai
According to the Regulations, target foreign R&D centers can be:
- A foreign-funded R&D center, which refers to an institution set up by foreign investors to engage in research, development, and experimental development (including intermediate experiments serving R&D activities) in natural sciences and related fields of science and technology, of which the content includes basic research, applied research, and product development;
- A global R&D center, which refers to a global-level R&D center established by foreign investors that possesses exclusively owned research and development technology platforms, undertakes key steps, and the majority of the process of its global-level R&D projects and the progress of its Shanghai R&D projects keep pace with comparable global activities; or
- A foreign-funded open innovation platform, which refers to a research and development center that promotes project-based cooperation with SMEs and innovation teams to realize co-innovation by providing facilities, equipment, research and development sites, and professional guidance and by leveraging the platform’s technology, talent, capital, data, and other resources.
For each of the three types of foreign R&D centers, certain conditions must be met, such as a minimum amount of investment in R&D, to be accredited as a qualified applicant. You may refer to the following table for details.
Eligible applicants can apply through “Government Online-Offline Shanghai” (Shanghai’s all-in-one online government service platform) and the government departments-in-charge will make a decision on whether or not to grant accreditation within five working days from receipt of the application materials.
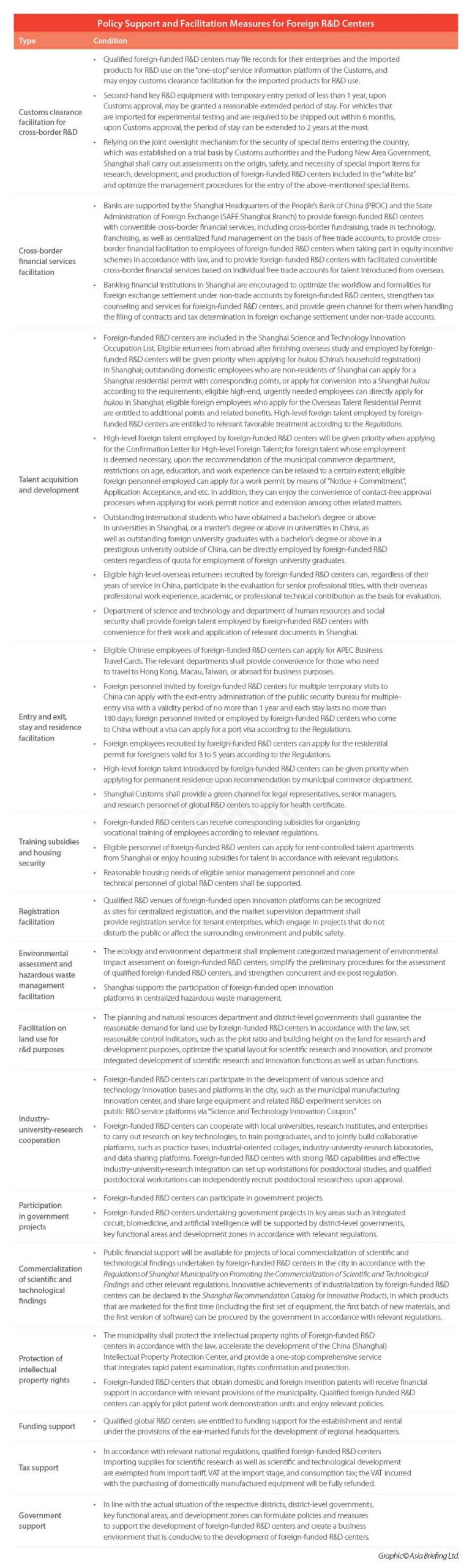
Policy support and facilitation measures for foreign R&D centers
Once identified as a foreign R&D center, a global R&D Center, or a foreign-funded open innovation platform, the applicant could enjoy access to various policy support measures.
Customs-wise, the Shanghai Customs has launched measures, such as facilitating the customs clearance for R&D supplies, implementing ‘white list’ management for the import of special items, and providing the green channel for R&D talents.
Qualified foreign R&D centers may file records for the enterprises and the imported goods for R&D use on the Customs’ one-stop service information platform to enjoy customs clearance facilitation for the products. Second-hand key R&D equipment imported for less than one year, upon Customs’ approval, may be granted a reasonable extended period of stay. Vehicles that are imported for experimental testing and are required to be shipped out within six months, upon the approval, can also be granted extended period of stay for no more than two years. For some special import items for R&D, Shanghai can carry out assessment of the source and safety of inbound special items and reasonable needs for R&D and production for foreign-funded R&D centers included in the ‘white list’ and optimizes the administrative procedures for the entry of the special items.
In cross-border financial services facilitation, banks are encouraged to provide foreign-funded R&D centers with convertible cross-border financial services, including cross-border fundraising, trade in technology, franchising, as well as centralized fund management on the basis of free trade accounts. They are also encouraged to provide cross-border financial facilitation to employees of foreign-funded R&D centers when taking part in equity incentive schemes in accordance with law and to provide foreign-funded R&D centers with facilitated convertible cross-border financial services based on individual free trade accounts for talent introduced from overseas.
In terms of tax support, qualified foreign-funded R&D centers that import scientific research and technological development supplies will be exempted from import duties, value-added tax (VAT), and consumption tax (CT) on imports, and the VAT will be refunded in full if they purchase domestically made equipment.
In addition, eligible global R&D centers can receive start-up and rental subsidies in accordance with the relevant provisions of the regional headquarters development special fund.
Foreign-funded R&D centers will also be encouraged to participate in government projects in key areas, such as integrated circuit, biomedicine, and artificial intelligence.
For more details, please refer to the following table:
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
We also maintain offices assisting foreign investors in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, United States, and Italy, in addition to our practices in India and Russia and our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative.
- Previous Article A New China for 2021: Foreign Investor Friendly Access, Overseas Direct Investment in Hi-Tech Projects and M&A, and More Belt & Road Initiative Opportunities
- Next Article China Clarifies Deadlines for Filing Tax Returns in 2021