Investing in Wuhan, Hubei Province: China City Spotlight
Wuhan city, situated in central China’s Hubei province, has emerged as a compelling investment destination, boasting a robust economy, a diverse range of industries, attractive incentives, and well-established preferential zones. This investment profile delves into the city’s key economic strengths, industrial ecosystem, supportive policies and incentives, and designated preferential zones, shedding light on the opportunities it offers to potential investors.
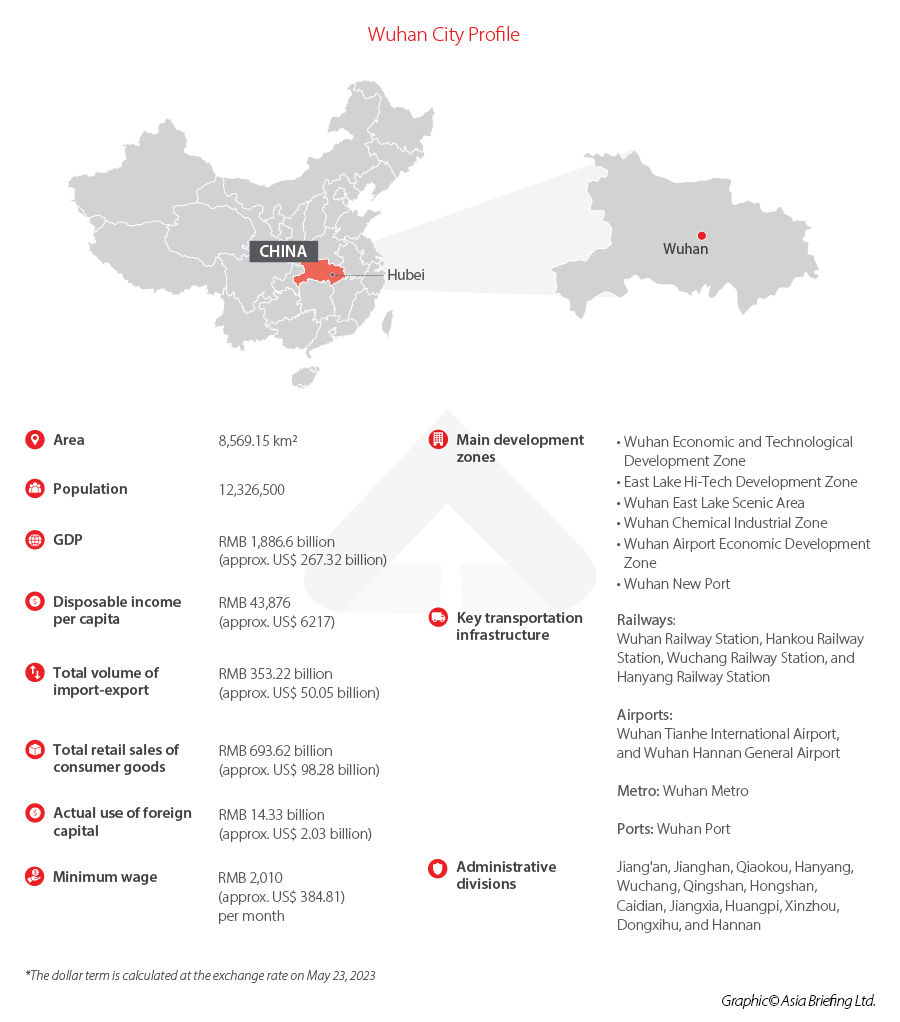
Wuhan, the capital city of Hubei province in Central China, stands as the largest urban center in the region. Situated along the majestic Yangtze River, the world’s third-longest river, Wuhan is geographically divided into three parts: Wuchang, Hankou, and Hanyang.
With a rich history as an economic, industrial, and transportation hub, Wuhan holds immense significance for both the local region and the country as a whole. It also serves as a prominent center for scientific, cultural, and educational pursuits in central China.
As of the end of 2022, Wuhan’s GDP contributes to a substantial 35 percent of Hubei province’s overall economic output. In recent years, the city has garnered significant attention from foreign enterprises, particularly in the field of new energy and intelligent network industries. Renowned companies like Amazon, Honda, Effie, Faurecia, Amberford, Visteon, and Cummins, have established their factories or research and development (R&D) centers in Wuhan, showcasing their confidence in the city’s potential.
Wuhan’s economic profile
In 2022, Wuhan’s GDP reached RMB 1,886.6 billion (approx. US$266.5 billion), with a year-on-year increase of 4.0 percent. Given the significant disruptions to the economy imposed by the COVID-19 outbreaks, this annual growth rate is decent although it’s mild as compared to previous years. Also, while Wuhan ranked eighth in the list of top 10 Chinese cities by GDP in 2022, it is important to highlight that Wuhan achieved the highest year-on-year GDP growth rate among these cities. This indicates the city’s strong economic potential for further development.
In the past year, Wuhan’s foreign trade witnessed a notable year-on-year increase of 5.3 percent, amounting to RMB 353.22 billion (approx. US$50.02 billion). Notably, Wuhan’s imports and exports through cross-border e-commerce alone reached RMB 8.88 billion (approx. US$1.257 billion), marking an impressive surge of 99.2 percent. This substantial growth presents promising opportunities for e-businesses engaged in cross-border trade.
In 2022, the actual utilized foreign capital in Wuhan reached RMB 14.33 billion (approx. US$2.03 billion), with a year-on-year growth rate of 2.9 percent. This amount accounted for 78.3 percent of the foreign capital utilized in Hubei province. Throughout the year, Wuhan saw the establishment of 285 new FIEs, further highlighting its attractiveness to foreign investors. To date, Wuhan has successfully attracted a total of 23 foreign company headquarters, bolstering its reputation as a preferred destination for international businesses.
Five advantages of investing in Wuhan
Superior transportation and logistic
Wuhan boasts the distinction of possessing the largest inland port along the Yangtze River. In the first quarter of 2023, Wuhan Port experienced a remarkable 160 percent increase in inbound and outbound vessel traffic compared to the same period last year. Furthermore, Wuhan stands as one of the four major railway hubs in China, playing a pivotal role in facilitating efficient transportation networks. Presently, the China-Europe Railway Express (Wuhan) operates an extensive network of 43 cross-border transportation routes, encompassing 107 cities across 40 countries spanning the Eurasian continent.
In recent years, Wuhan has emerged as a crucial node for multiple international transportation corridors, including the “Japan-Wuhan-Europe,” “Japan-Wuhan-Mongolia,” “Belarus-Wuhan,” and “Europe-Wuhan-Hong Kong” routes. These strategic routes have been deeply integrated into the national initiatives of both the Belt and Road Initiative and the Yangtze River Economic Belt, reflecting Wuhan’s integral role in advancing regional connectivity and fostering international trade relationships.
Education and science strength
In the 2021 rankings of Chinese cities for sci-tech innovation, Wuhan secured an impressive fifth position, as determined by the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS). This recognition highlights Wuhan’s significant contributions to the field of scientific and technological advancements. Notably, the city hosts an impressive network of 92 universities and accommodates nearly 1.3 million college students, solidifying its position as the world’s top-ranking city in terms of student population.
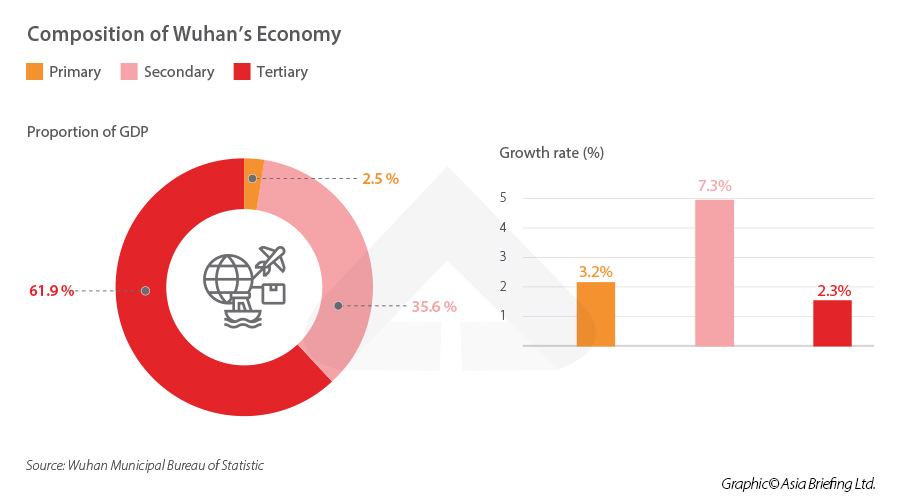
There are a total of 12,400 high-tech enterprises, reflecting a vibrant and dynamic environment for innovation. The value added by the high-tech industry reached a substantial RMB 5321.1 billion (approx. US$753.6 billion) in 2022, constituting 28.2 percent of the city’s GDP. This figure further underscores Wuhan’s pivotal role in driving technological progress and economic growth.
Internationalization
Wuhan accommodates a total of four foreign consulates and 23 foreign trade and economic organizations. It also has established relations with a network of 28 international sister cities and 90 cities for international friendly exchanges. By the end of 2022, 309 out of the Global Fortune 500 companies had set up headquarters or offices in Wuhan.
This significant influx of global industry leaders highlights Wuhan’s appeal as a favorable business environment and a hub for international investment and collaboration.
Solid industrial foundation
Wuhan, with its solid industrial foundation, is poised for a promising future in terms of development. The city boasts five industrial bases and three international industrial parks that drive innovation, technological advancement, and economic growth across various sectors, positioning Wuhan as a hub for cutting-edge industries and fostering international collaboration.
- The National Memory Chip Base – with a projected production capacity of 300,000 chips/month in 2023, the memory base project can drive the development of chip design, packaging, manufacturing, and application.
- The National Aerospace Industry Base – it stimulates the development of independent and controllable information technology, aerospace cloud manufacturing, and new aerospace materials.
- The National NEV (New Energy Vehicle) and ICV (Intelligent and Connected Vehicle) Base – it promotes innovation and development in the NEV and ICV sectors, including intelligent vehicle chip, in-car intelligent operating system, high-precision mapping, driver assistance system, and autonomous driving system.
- The National cybersecurity talent and Innovation Base – it promotes the cybersecurity capabilities and resilience of the digital sector.
- The Health Industry Base – it stimulates the coordinated development of major healthcare fields, including biomedicine, medical equipment, medicine, distribution, bio-agriculture, and health services.
- Sino-French Wuhan Ecological Demonstration City – it stimulates the application of ecological and environmental technologies, including renewable energy, low-carbon transportation system, and green buildings.
- Wuhan Sino-German Industrial Park – it focuses on new energy vehicles, intelligent and connected vehicles, intelligent manufacturing, electronic information technology and modern logistics.
- Wuhan Sino-Japanese Industrial Park – it focuses on aviation manufacturing, intelligent equipment, finance, cultural and creative industries, information services, and intelligent logistics.
Supportive policies for FDI in Wuhan
Each development zone within Wuhan provides an array of supportive policies aimed at attracting and facilitating the establishment and growth of foreign companies. Notably, Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone (ETDZ) and East Lake High-tech Development Zone (ELHDZ) have released their latest FDI policies in 2022.
These policies encompass reduced tax rates, rewards for foreign investment, talent incentives, and more. Below, we demonstrate the supportive FDI policies in Wuhan by outlining some of the current incentive policies offered in these two development zones as examples.
Rewards for foreign investment and foreign high-end talents
In line with other cities, the development zones in Wuhan provide various incentives for foreign investment and talent attraction.
For instance, both in ETDZ and ELHDZ, foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) with newly increased paid-in registered capital of US$3 million, US$10 million, or US$30 million will receive rewards equivalent to 2 percent, 4 percent, and 6 percent of their paid-up capital, respectively. The maximum reward amount for a single enterprise can reach up to RMB 25 million (approx. US$3.54 million) in ETDZ and RMB 20 million (approx. US$2.83 million) in ELHDZ.
Besides, qualified foreign talents working in ELHDZ can get annual subsidies equal to RMB 100,000 (approx. US$14,162.5). The local government also offers streamlined processes and conveniences for foreign talents, including assistance with housing, visa application, and work permit application.
Tax credits for qualified FIEs
In addition to monetary rewards, Wuhan offers generous tax credits to qualified foreign investments.
Take EDTZ as an example. According to the Regulations of Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, released in June 2021, a set of preferential tax policies are available to eligible FIEs.
- CIT reduction and exemption
Within the development zone, productive FIEs are eligible for a reduced corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 15 percent, as compared to the standard CIT rate of 25 percent. For productive FIEs with a planned operating period of more than 10 years, it shall enjoy CIT exemption for the first two years (starting from the first income-generating year), and a halved CIT rate (that is, 12.5 percent) in the subsequent three years.
Upon the expiration of the CIT reduction or exemption period aforementioned, where the output value of the productive FIE’s export products of the current year reaches more than 70 percent of its annual total output value, the CIT shall be paid at a reduced rate of 10 percent. Besides, advanced technology enterprises are eligible for an additional 3-year extension to pay CIT at a reduced rate of 10 percent.
- Income tax refund
Foreign investors who reinvest their share of profits directly back into the same enterprise, increase registered capital, or use it as capital to establish other FIE, may be eligible for a tax refund.
If the reinvestment is maintained for a minimum of 5 years, 40 percent of the income tax paid on the reinvested portion can be refunded. For enterprises directly engaged in organizing or expanding the export of products or classified as advanced technology enterprises, with an operating period of no less than 5 years, the entire amount of income tax paid on the reinvested portion can be refunded.
- Other tax incentives
The EDTZ also provides preferential tax treatment when foreign investors remitting their profits overseas; when FIEs purchase or build newly built houses; and when import certain materials, equipment, vehicles, and office supplies within the scope.
Structure of subsidies
As demonstrated below, foreign inventors in Wuhan can benefit from a series of other subsidies, such as:
- Interest subsidies for self-use loans obtained from domestic banks: FIEs in ETDZ will receive interest subsidies equivalent to 30 percent of the loan interest, while in ELHDZ, they will receive interest subsidies equivalent to 25 percent of the loan interest. The total annual subsidy amount for a single enterprise can reach up to RMB 3 million (approximately US$0.42 million) in both zones.
- Promotion of R&D center establishment: FIEs establishing R&D centers can receive incentive support equivalent to 10 percent of their annual actual R&D expenditure. In ELHDZ, the total annual subsidy amount is capped at RMB 2 million (approx. US$0.28 million), while in ETDZ, it can reach up to RMB 3 million (approx. US$0.42 million).
- Office/factory space subsidies: FIEs that purchase self-used factories or self-used office buildings in EDTZ will be given a subsidy of 10 percent of the actual amount paid, and the accumulated amount of subsidies enjoyed by a single enterprise will not exceed RMB 10 million (approx. US$1.41 million). For FIEs that rent a new self-use workshop of 500 square meters or larger in EDTZ, a subsidy will be granted that is equal to 80 percent of the contract rent price. The maximum subsidy term is three years, and the total annual subsidy amount is not more than RMB 3 million (approx. US$0.42 million). For FIEs renting office space for their own use, they shall be subsidized by 50 percent of the contract rent price for the part below 1,000 square meters, and 30 percent of the contract rent price for the part over 1000 square meters. The subsidy period shall not exceed 3 years, and the total amount of the annual subsidy shall not exceed RMB 3 million (approx. US$0.42 million).
- Fixed asset investment incentives: For FIEs whose actual investment in fixed assets reaches US$5 million or equivalent currency, they shall be given a reward of 8 percent of the actual investment in fixed assets, and the accumulative amount of subsidies enjoyed by a single enterprise shall not exceed RMB 35 million (approx. US$4.95 million).
- Support for headquarter: FIEs that establish their headquarters or regional headquarters in ELHDZ will be eligible for a one-time reward of RMB 1 million (approximately US$0.24 million). In ETDZ, the subsidy can reach up to RMB 3 million (approximately US$0.42 million).
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China’s Social Credit System: Scope of Information Collection and Punishments for Untrustworthy Entities
- Next Article Australische Exporte nach China auf Rekordhöhe wecken Optimismus für bilateralen Handel