Investing in Nanjing: Industry, Economics, and Policy
Nanjing (南京) is the capital city of China’s Jiangsu Province, and it holds a meaningful spot in Chinese history and culture. The city served as the national capital for numerous centuries and is considered one of the four ancient capitals in Chinese dynastic history. Nanjing is also one of China’s fifteen sub-provincial cities.
Set against a backdrop of rich history and cultural heritage, modern-day Nanjing is an economically competitive metropolis with established manufacturing and service industries. To this day, the city functions as a national hub of education, research, transportation, and trade. It is also the second largest city in the East China region (behind only Shanghai), with a population of over nine million people. Located in the Yangtze River Delta region, one of the most important supercity clusters in China, Nanjing’s geographical position has also contributed to its significance.
These factors have helped Nanjing become a hotspot for foreign investors who also seek to capitalize on its strategic placement as a hub for research and development (R&D) and innovation.
In this article, we provide an overview of Nanjing’s economic and industrial development and discuss the benefits of investing in this rapidly growing region.

Economic Overview
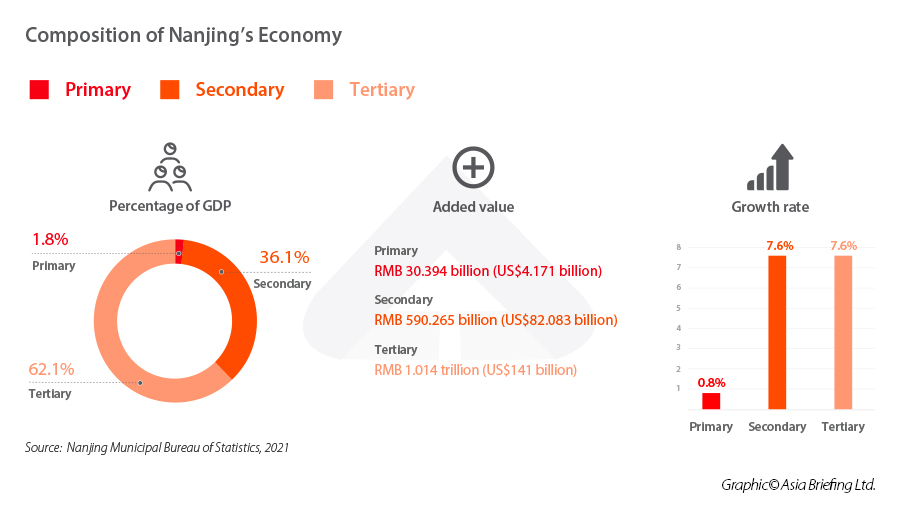
Nanjing is a vital regional commercial hub with a thriving local and international business community. Its GDP increased by 7.5 percent in 2021, reaching RMB 1.63 trillion (US$227.36 billion).
Electronics, steel production, petrochemicals, vehicle manufacture, information technology, photovoltaic, rail transportation, banking, and tourism are among the city’s most developed industries. While cultivating the expansion of these traditional industries, Nanjing is also creating strategic industries in several pivotal sectors, focusing on those with annual growth rates of more than 20 percent, which include high-end equipment manufacturing, biomedicine, new energy vehicles, smart grids, energy conservation, and environmental protection.
Nanjing is a service-driven economy, with the tertiary sector accounting for almost 63 percent of the GDP. Manufacturing nonetheless remains an important mainstay industry, accounting for almost all of the remaining value-add to GDP.
Nanjing is considered among the top cities serving as engines for development in the region. As of 2020, the city had invested more than RMB 40 billion (US$5.69 billion) in R&D. By 2021, the city had become home to 128 high-tech firms. Biopharmaceuticals, energy conservation, and novel materials accounted for around 34 percent of these, and 20 percent of them established their headquarters in Jiangbei New Area.
Foreign trade and investment
The actual use of foreign capital in 2021 amounted to US$5.01 billion, a year-on-year increase of 11.1 percent. Nanjing has attracted approximately 10,000 foreign-invested firms since China’s reform and opening up. Over 80 of the top Fortune 500 companies have invested in nearly 150 projects in Nanjing, including BASF GROUP, Siemens, Bayer, and Thyssen Krupp from Germany; Carrefour and Auchan from France; Shell and Phillips from the Netherlands; BP and Tesco from the United Kingdom; Ericsson from Sweden; Fiat from Italy; Ford, Motorola, Best Buy, Kimberly-Clark, Emerson, and Morgan Chase from the United States.
Nanjing’s overall import-export value in 2021 was RMB 636.68 billion (US$88.14 billion), representing a 19.2 percent increase over 2020. Exports contributed RMB 398.98 billion (US$55.23 billion), an annual increase of 17.4 percent.
The city’s main trading partners are the European Union (EU), ASEAN, the US, South Korea, and Japan. Of these, the city’s trade with the ASEAN block increased by 32.1 percent year-on-year, the highest margin compared to that of the other partners.
Singapore-Nanjing cooperation
Singapore is among Nanjing’s leading trading and investment partners. The Singapore-Nanjing Special Projects Cooperation Panel (SNCP) established by the Singapore-Jiangsu Collaboration Council (SJCC) serves as a city-level forum to strengthen bilateral cooperation in special projects in Nanjing. This collaboration is manifested through examples such as the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) cosigned between the Singapore-based Luye Medical Group Pte. Ltd and the Singapore Nanjing Eco Hi-Tech Island Development Co Ltd to develop a high-end integrated hospital on Singapore Nanjing Eco Hi-Tech Island (a township development project created in collaboration between Singapore’s Ministry of Trade and Industry, the CPC Jiangsu Committee, and the Jiangsu provincial government) to provide private healthcare to the city’s residents.
The island extends for 15.21 square kilometers and represents a ‘new model of Sino-Singapore cooperation, as well as a model of sustainable cities of innovation, entrepreneurship, and city-industry integration,’ with the goal of becoming ‘an incomparable Eco Hi-tech city, Low Carbon Smart Island.’
Industry development
Integrated circuit
The ecology of Nanjing’s integrated circuit (IC) sector has largely taken shape, encompassing the industrial chains of chip design, wafer production, packaging and testing, equipment, materials, and critical upstream and downstream linkages. As of 2021, Nanjing has attracted over 400 IC-related businesses, and its main business revenue surged by more than 40 percent year on year.
The city puts major emphasis on the development of industries such as IC, electronic design platforms (EDA tools), IP databases, central processing units (CPU), microcontrollers (MCU), digital signal processors (DSP), communication chips, digital TV chips, multimedia chips, information security and video monitoring chips, and MEMS sensor chips, among others.
New energy vehicles
Nanjing has effectively established a whole production chain for new energy vehicles (NEVs). The sector has begun to take shape with the manufacture of whole automobiles, batteries and electric accessories, pure electric vehicle powertrains, and automotive air conditioners. The industrial scale is the most extensive in the province. To fully support the NEV industry’s growth, at the end of 2018, the General Office of Nanjing Municipal Government issued the Action Plan for Building a Landmark of New Energy Automobile Industry in Nanjing, pointing out that, by 2025, the city’s NEV output will rank among the top three cities in the country, with revenue of RMB 300 billion (US$41.66 billion).
To achieve this goal, the Nanjing Municipal Government has spearheaded the development of an industrial public service platform, providing full support to organization and leadership, talent support, financial innovation, and financial assistance, while also expanding efforts to attract investment. Four NEV industrial bases have been launched in the Jiangbei New Area to attract investments, and NEV companies in each base have progressively expanded. Pukou Economic Development Zone, for example, is home to SAIC New Energy, Yuebo Power, Zhidou Automobile, and Bojun Automobile, whereas Nanjing Economic Development Zone is home to Baiteng, Great Wall Huaguan, Xilai XPT, LG Chemistry, among others.
New medicine and life health
Nanjing has established eight state-level biomedical innovation centers, including the National Health and Medical Big Data (Nanjing) Center, the National Genetic Engineering Mouse Resource Bank, and 15 national engineering centers (laboratories). The city ranked at fourth place nationally in terms of bio-medicine development. At the same time, Nanjing boasts more than 20 bio-medicine schools and institutions, including China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Nanjing University, and the number of basic talents output ranks first in the country. In 2021, the biopharmaceutical sector maintained its rapid expansion, with a major business revenue of RMB 40 billion (US$5.55 billion) and a year-on-year increase of over 20 percent.
Software and information services
With 820,000 personnel, 5,300 significant organizations, and 120 publicly traded companies, Nanjing is considered China’s ‘Software City.’ Most of Nanjing’s colleges and universities offer degrees related to computer science and software engineering.
Nanjing’s software business revenue topped RMB 510 billion (US$70.83 billion) in 2021, and its industrial scale ranked first – both province- and country-wide. Autonomous operating systems, databases, middleware, and office software are examples of key products in this sector. Nanjing also supports the application of cloud computing, big data, blockchain, large cloud computing service platforms, advanced manufacturing, data circulation, and other technologies.
Artificial intelligence
Nanjing has attracted over 300 artificial intelligence (AI) research and development and application firms, covering various fields, such as the basic, technical, and application layers of AI. It has gained certain benefits in the areas of intelligent software, intelligent sensors, intelligent chips, and intelligent robotics. According to the 2020 AI Ecosystem in China White Paper report, Nanjing classifies among the top 10 cities in terms of the overall innovative environment. The industrial scale of the city’s artificial intelligence sector surpassed RMB 8 billion (US$1.11 billion) in 2021.
Policies and trends
On April 9, 2021, the Nanjing Municipal Party Committee and the Nanjing Municipal Government jointly released the 14th Five-Year Plan for Nanjing’s National Economic and Social Development and the Outline of the Vision for 2035.
The plan promises to transform Nanjing into an innovative city with global influence while exploring new paths for green and low-carbon development. The city is projected to become a megacity with a permanent population exceeding 10 million people and an economic aggregate of RMB 2 trillion (US$277 billion) by 2035.
To achieve this, the government has built 15 high-tech zones across all administrative areas, 12 of which are located in the city center. Leading firms such as Huawei, ZTE, and TSMC, have established their headquarters there, causing mid-stream and downstream enterprises to build an industrial agglomeration, resulting in the formation of a new ecosystem
Incentive policies for foreign investment in Nanjing
Nanjing is among mainland China’s most business-friendly cities. In 2019, the city’s Municipal Government released a document titled Opinions of Nanjing Municipal Government on Several Measures for Further Opening up and Accelerating the Use of Foreign Capital, which includes a wide range of beneficial policies for foreign companies who seek to set up and expand in the area. Below we list some of the incentive policies currently available in Nanjing.
Support for R&D activities
The Municipal Government will support foreign companies to set up R&D institutions, engineering centers, technology centers, and key laboratories in the city, by providing up to RMB 2 million (US$276,901) in financing. In the case of multinational companies establishing R&D institutions in Nanjing, they are eligible for a maximum of RMB 5 million (US$692,252), according to their annual R&D investment and the size of specialized personnel.
Foreign R&D centers are exempted from customs duties, import value-added tax, and consumption tax on the import of supplies needed for scientific research and technological development. They are also eligible for full refunds of the value-added tax on the purchase of domestic equipment.
Subsidies for foreign talents
The Municipal Government supports the inclusion of foreign talents and innovative entrepreneurs in scientific research and development projects based in Nanjing, according to the Reference Catalogue for the Introduction of Overseas High-level Talents by the State (2016). Experts covered under the Nanjing Talent Plan for Entrepreneurship are eligible for funding of up to RMB 10 million (US$1.38 million) for achievement in industrial scientific research. Those who have obtained venture capital for their successful projects are entitled to a follow-up investment of a maximum of RMB 100 million (US$13.85 million)
Foreign talents who have been recognized by the competent talent department can apply for a five-year valid work-type residence permit.
Incentives for headquartering in Nanjing
Foreign companies that establish regional headquarters in Nanjing are eligible for a start-up subsidy of up to RMB 5 million (US$692,319) to be distributed in three installments of 40 percent, 30 percent, and 30 percent, respectively.
Nanjing key development areas
Nanjing Economic and Technological Development Zone
The Nanjing Economic and Technological Development Zone is composed of three state-level platforms, namely the Nanjing Comprehensive Bonded Zone (NJCBZ), the Xingang High-tech Park, and the Nanjing Port-Based National Logistics Hub.
Since its inception 20 years ago, the Nanjing Economic and Technological Development Zone has attracted over RMB 180 billion (US$24.99 billion) in domestic and foreign investment, with the annual industrial output value of its major sectors exceeding RMB 100 billion (US$13.88 billion). The area’s total investment environment was ranked first among national economic and technology development zones.
The zone relies on Longtan Deepwater Port as an important hub of the Yangtze River’s river-sea inter-modal transportation. Additionally, the Xianlin Science City also facilitates the growth of urban, scientific, and educational resource capacity, focusing on the development of industries such as optoelectronic display, bio-medicine, high-end equipment, modern logistics, and technology services.
Jiangning Economic and Technological Development Zone
Established in June 1992 in Nanjing’s Jiangning district, the Jiangning Economic and Technological Development Zone is a state-level economic and technological development zone, a high-level innovative entrepreneurial center for overseas talents, and it has the highest degree of smart grid industry agglomeration. More than 100 smart grid companies, including Nanrui Group, Guodian Nanjing Automation Co.,Ltd, Siemens, ABB, and NR ELECTRIC, have gathered here to establish a complete industrial chain of six links, including generation, transmission, transformation, distribution, power consumption, and dispatching.
A wind power industrial park, a bonded logistics park, an electric power automation industrial base, and an aviation power industrial base are among the 10 industrial platforms located in the zone. Since its establishment, the zone has introduced more than 1,800 enterprises, among which 437 are foreign-funded, including 45 fortune 500 enterprises such as Ford, Mazda, Ericsson, Siemens, Motorola, and Hitachi. As of 2021, the zone has invested a total of US$9.6 billion in contracted foreign capital and over US$5.5 billion in actual investment.
Jiangning High-Tech Development Zone
Jiangning High-Tech Development Zone is in the heart of Nanjing’s Jiangning District. Established on June 2, 1994, it became China’s first development park to blend a high-tech industrial zone, a university town, and a picturesque tourism resort, with an overall planning area of 195 square kilometers.
The zone is a major component of the National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone in Southern Jiangsu Province’s “8+1” core system. It was later designated as a national innovative characteristic park, talent training demonstration base, and an area for the development of the bio-pharmaceutical industry. Because of this, the Jiangning Hi-tech Development Zone shows significant advantages in terms of science and education resources, being home to 16 universities, such as China Pharmaceutical University and Nanjing Medical University, as well as several research institutes, such as the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Software Research Institute. It has established 27 engineering and technology centers, eight postdoctoral workstations, and two provincial incubators, with the result of having a consistent concentration of top talent.
The area has clear advantages in certain industries, creating a pattern of industrial growth dominated by life science, high-end intelligent manufacturing, and the contemporary service industry. As of 2021, about 250 life science companies have settled in the area, and numerous treatments have been developed, including monoclonal antibodies, anti-AIDS, anti-tumor, and xenotransplantation.
The industrial park is crossed by the Nanjing Metro Line 1, the Nanjing Ring Expressway, the Nanjing Hangzhou Expressway, the Nanjing Hangzhou high-speed train, and the 104 National Highway.
Nanjing Jiangbei New Area
Established in 2015 by the State Council, the Nanjing Jiangbei New Area became the thirteenth state-level new area in Jiangsu province.
In 2021, the new district achieved a total industrial output value of RMB 239 billion (US$19.30 billion). Total society fixed asset investment was RMB 55.9 billion (US$7.76 billion), with a year-on-year increase of 12.5 percent, and per capita disposable income of urban households exceeded RMB 61,000 (US$8,461), with a growth of 18.6 percent from when the area was established.
Since its establishment, the new district has become home to over 300 enterprises, with an output value exceeding RMB 50 billion (US$6.94 billion ), with the overall scale of the life and health industry being close to RMB 100 billion (US$13.88 billion) and a focus on precision medicine.
Why should you invest in Nanjing?
All in all, there are several factors why foreign businesses may establish themselves in Nanjing. These include:
- Government assistance: Nanjing government has created a simplified international business services platform to meet the diverse demands of enterprises entering China. This includes assistance with company growth, corporate and intellectual property registration, grant contests, and other services.
- Location: Nanjing is in a good geographical location, with high-speed train connections to Shanghai, Hangzhou, Wuhan, Ningbo, Beijing, and Tianjin. In addition, it is home to the world’s largest inland port.
- Talent pool: Nanjing is a southern Chinese educational hub that graduates 250,000 students each year from more than 60 institutions. Nanjing University is one of the top five institutions in China.
- Quality of life: International K-12 schools, Jiangsu province’s best hospital system, international chambers of commerce for the EU, USA, and Australia, international retail franchisees, and centrally located English-speaking entertainment districts are all available to the international business community in Nanjing.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article In che modo il precedente Congresso del Partito Comunista ha programmato lo sviluppo economico, politico e normativo della Cina?
- Next Article Sustainable Fashion in China: An Emerging Trend in the Apparel Industry







