COVID-19 Catalyzes Commercial Use of 5G in China
China is stepping up its 5G network construction as part of “new infrastructure” investments to spur its virus-hit economy and meet the long-term goal of becoming a leading high-tech innovator.
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) expects the country to build and operate 600,000 5G base stations by the end of this year. At the end of Q1 2020, China had already established 198,000 5G base stations, covering over 50 cities.
If in previous years China was using national power to drive the realization of 5G, and Chinese 5G operators were worried about the commercial use and profit model of 5G – the outbreak of COVID-19 has dramatically changed prospects. The outbreak has driven a major chunk of the workforce online, and made inevitable the huge market prospects for 5G network investments and enabled technologies.
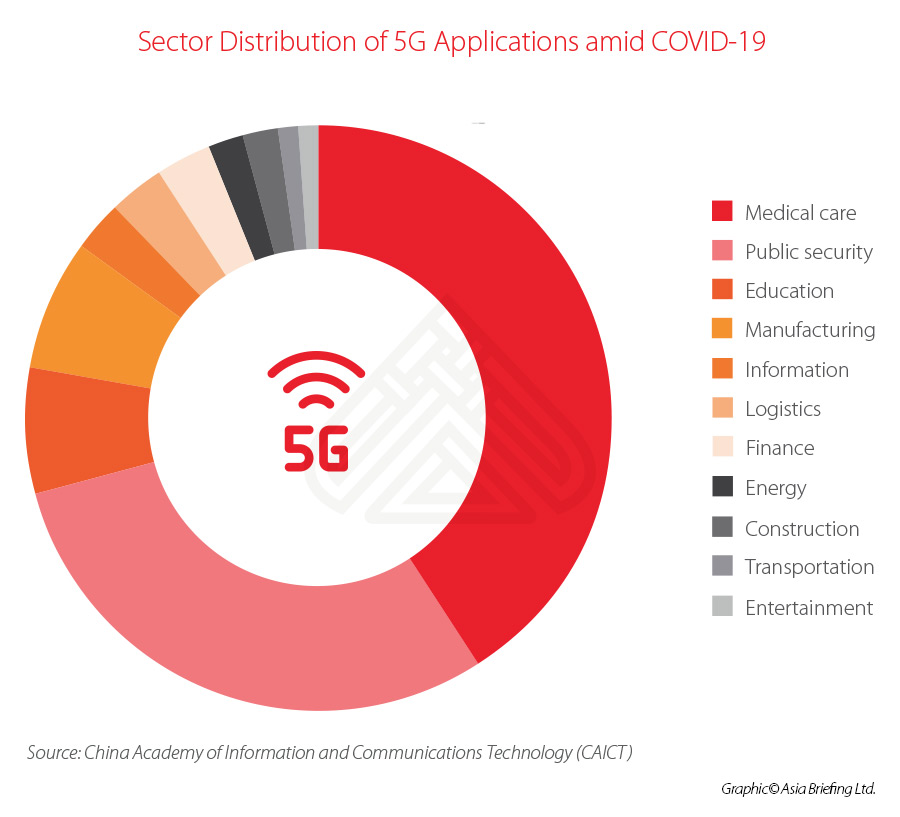
Since the beginning of the epidemic, China has witnessed the faster and more extensive use of 5G in various fields. According to a report from China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), 5G applications were used heavily in the medical care, public security, education, manufacturing, and logistics sectors amid the COVID-19 outbreak.
Statistics show that 22 Chinese provinces and cities implemented 5G applications to combat COVID-19. Among them, the provinces of Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Jiangsu as well as Beijing, Shanghai, and Wuhan, the former epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak, are now the main hubs for 5G application trials.
In this article, we briefly track how the increased application of 5G amid the coronavirus outbreak has impacted China’s leading and new frontier industries.
Telemedicine and healthcare
Since the epidemic exposed major flaws in China’s existing healthcare system, an opportunity arose to suddenly shift to 5G applications to conduct large trials in the healthcare sector.
5G-powered telemedicine, remote CT scanning, and remote ultrasound testing were utilized to tackle the shortage of medical personnel in the worst-hit areas and avoid person to person transmission of infection.
It is reported that during the coronavirus outbreak, more than 100 hospitals used 5G systems for telemedicine consultation.
For instance, the West China Hospital in Sichuan province, together with China Telecom, completed remote CT scans and offered teleconsultation services to COVID-19 patients, by leveraging the use of 5G double gigabit and remote CT scanner.
The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University in Yunnan province, together with China Mobile, launched a 5G-based online platform to provide free COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment.
Beijing JinCheng Medical Technology, a medical equipment company, provided hospitals in Wuhan with a CT and X-ray coordination solution based on 5G cloud collaboration, which addressed the shortage of radiologists, thereby improving efficiency in screening suspected COVID-19 cases.
CloudMinds Technology, a SoftBank-backed startup in Beijing, donated robots with 5G-enabled cloud-based systems to Wuhan’s hospitals. The robots worked 24/7 hours and undertook jobs like remote nursing, body temperature taking, heart rates and blood oxygen levels measurement, medication delivery, disinfection, and cleaning.
Besides, doctors from the People’s Hospital of Zhejiang even used 5G to remotely control a robot to perform an ultrasound test on a COVID-19 patient at a hospital in Wuhan from 700 kilometers away.
Mass surveillance and public security
Infrared temperature measurement based on 5G are now being massively applied to traffic hubs in a number of China’s cities to monitor the condition of passengers.
Recently, on May 15, China Mobile coordinated with the local education authorities in Hubei province and provided 449 5G-powered infrared thermal imaging temperature measuring equipment to 321 schools. Based on the low-latency 5G and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, the equipment can detect body temperature at a distance of 10 meters, implement face tracking, and measure multiple people at the same time and up to 500 people per minute.
Besides schools, this kind of 5G infrared thermal imaging temperature measurement has also been used in densely populated places like hotels, entertainment venues, shopping malls, and supermarkets.
Cloud live streaming
During the COVID-19 outbreak, 65 million internet users who stayed at home witnessed the setting up of Wuhan’s two major temporary hospitals – “Huoshenshan” (Fire God Mountain) and “leishenshan” (Thunder God Mountain) through around-the-clock 5G live streaming.
Hubei Radio and Television Station, using the 5G network of China Broadcasting Network Corporation, provided a network-wide live broadcast of press conferences on epidemic control in Hubei Province. As of April 8, the television station had broadcasted 56 press conferences, which contacted more than 140 domestic and overseas journalists, synced the content to nearly 200 media, and were enabled with remote Q&A function.
We expect that, along with the spread of 5G networks, the technology will keep fueling the livestreaming industry, which will propel other industries, especially online shopping, online entertainment, and online education.
In fact, the education industry has led the way, with millions of students stuck at home. According to Nikkei Asian Review, during the outbreak, newly deployed 5G networks have helped online education providers broadcast more than 1.57 million classes. In several Beijing high schools, teachers even conducted exams remotely using cloud computing.
Manufacturing
The first mass beneficiary of 5G in manufacturing will be 5G handset manufacturers. The signs of a recovery in smartphone markets has shown up – by the end of March 2020, the shipment of China-made 5G phones reached 26 million, and 76 types of 5G mobile phones were produced. Chinese brands captured 61 percent of global 5G smartphone shipment in the first quarter of 2020.
In addition, in terms of smart cars, it is reported that Huawei will partner with 18 carmakers, including FAW group, BYD, and T3 Mobility, to build a 5G-enabled automobile ecosystem. This move should accelerate the uptake of 5G technology in smart cars, injecting much needed vitality to the currently struggling automobile market.
Transportation and logistics
In Yunnan province, 5G drones were used to patrol and advice people to avoid gatherings. Near the Beijing National Stadium, 5G drones dispatched face masks and delivered hot meals to hospital patients from 1,800 km away. In Hubei, the 5G drones even circled the skies, spraying disinfectants.
What’s more, smart ports – automated ports that use nascent technologies like big data, 5G, IoT, and blockchain solutions to improve performance – are emerging. COSCO Shipping, Dongfeng Motor Corporation, and China Mobile jointly launched “smart port enabled by 5G and self-driving technology” in Beijing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Shiyan, Hong Kong, and Xiamen, on March 11. In Shenzhen, Huawei, CMPort, China Mobile with other 11 partners established the first “5G smart port” innovation laboratory, planning to build a benchmark 5G smart port for the Greater Bay Area (GBA).
China has made 5G connectivity, innovation a priority
Since the economy is slowing down – China’s GDP shrank by 6.8 percent year-on-year in the first quarter – it may be unclear whether private businesses will be able to finance the upgrades for 5G routers in the immediate post-COVID-19 era.
Yet, regardless of its ongoing trade tensions with the US, China is not backing off promoting key technologies – following “Made in China 2025,” it is set to release “China Standards 2035” to ensure it has a seat at the table in the groups and institutions that will frame international standards on new emerging technologies.
Moving forward, sooner or later, 5G will be more extensively applied to life, production, and social governance. The increased roll-out of 5G networks, innovative 5G applications, and the integration of 5G technology with other technologies will result in mushrooming opportunities for foreign investors in China across industry and market commerce.
To round up, it is expected that the following sectors will see immediate and major dividends in the 5G era:
- Industrial chain of 5G consumer equipment: This will include the upstream and downstream industrial chain of 5G mobile phones (mobile phone manufacturers, mobile phone component manufacturers, and mobile phone vendors) and wearable equipment (VR glasses, helmet, 5G watches, etc.).
- Virtual world application development: This includes VR games, VR movies, virtual meeting apps, and IoT intelligence community.
- Traditional industries: This includes medical care, education, retail, manufacturing, services, and logistics, all of which will need to adapt to radical digital transformation or the application of new technologies.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
We also maintain offices assisting foreign investors in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, United States, and Italy, in addition to our practices in India and Russia and our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative.
- Previous Article China’s Two Sessions 2020: What Have We Learnt So Far
- Next Article China’s Travel Restrictions – Special Visa Applications